
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Aug 22, 2023
Velina describes herself as passionate media savvy and a versatile individual with numerous differen... | See full bio
April is a proficient content writer with a knack for research and communication. With a keen eye fo... | See full bio
3D Printing is a process that transforms digital designs into physical objects. It has gained popularity because of its affordable starting price of around $300. It is also small and easy to operate, which enables many people to access and create more designs and products.
Whether it's designing custom phone cases, intricate home decor items, personalized gifts, or even fashion accessories, a 3D printer can bring your unique ideas to life.
If you want to learn more about 3D Printing, look no further! This article provides 17 awesome ideas that you can make using 3D Printing.
🔑Key Takeaways
|
The fundamentals of the 3D Printing process involves four steps: modeling, slicing, printing, and post-processing. |
|
|
Many objects can be made using 3D Printing, some for spare and replacement, conceptual models, prototypes, jewelry, and others. |
|
|
There are a lot of industries benefitting from using 3D Printing. These include the food, construction, and education industry. |
|
|
3D Printing has become significant in producing new technologies for Medicine. Organs, body parts, and surgical models are more accessible using 3D Printing. |
|
|
There are many benefits associated with 3D Printing. It is cost-effective, has fast reproduction, and produces a high-quality product. |
A typical 3D printer operates similarly to an inkjet printer connected to a computer. It constructs a 3D model by adding a material layer at a time, starting from the bottom and moving upward.
The process involves four steps: modeling, slicing, printing, and post-processing. Modeling converts an object into a digital model that can be 3D printed. You can create models using 3D modeling software or download existing STL files.
The ideaMaker slices the model, allowing the 3D printer to calculate the route and filament required for printing. Next, the GCode generates a file and uploads a slice file to the printer.
You can observe this process through a transparent panel on a Raise3D Pro2 Series printer. Lastly, it will be post-processed, where parts will be removed and sanded.
|
👍Helpful Articles: To learn more about 3D Printing, check out Techjury’s articles on: |
Learn more about the objects you can make using 3D Printing.
Advancements in 3D Printing technology enabled the production of functional objects using templates, allowing for endless possibilities in the design and printing of virtually anything.
3D Printing offers incredible objects through groundbreaking techniques. Here are some of the extraordinary things you can do.
3D Printing can be used for digital manufacturing, allowing spare parts to be stored virtually and produced when needed, reducing storage costs and improving service.
 Image Source: Formslab
Image Source: Formslab
It is a powerful solution for addressing supply chain disruptions and spare parts availability by replacing extensive inventories with on-demand production. It can create the following;
It is more cost-effective for low-volume production than traditional manufacturing processes because it has lower fixed costs and does not require expensive tooling. This method is advantageous for those who want to replace or create small volumes of parts.
Concept modeling is a powerful communication tool for designers, architects, and engineers. It allows them to test, refine, and perfect your ideas without the limitations of traditional methods.
Hyper-realistic concept models convey your vision and excitement effectively, enhancing communication with your team, clients, and leadership.
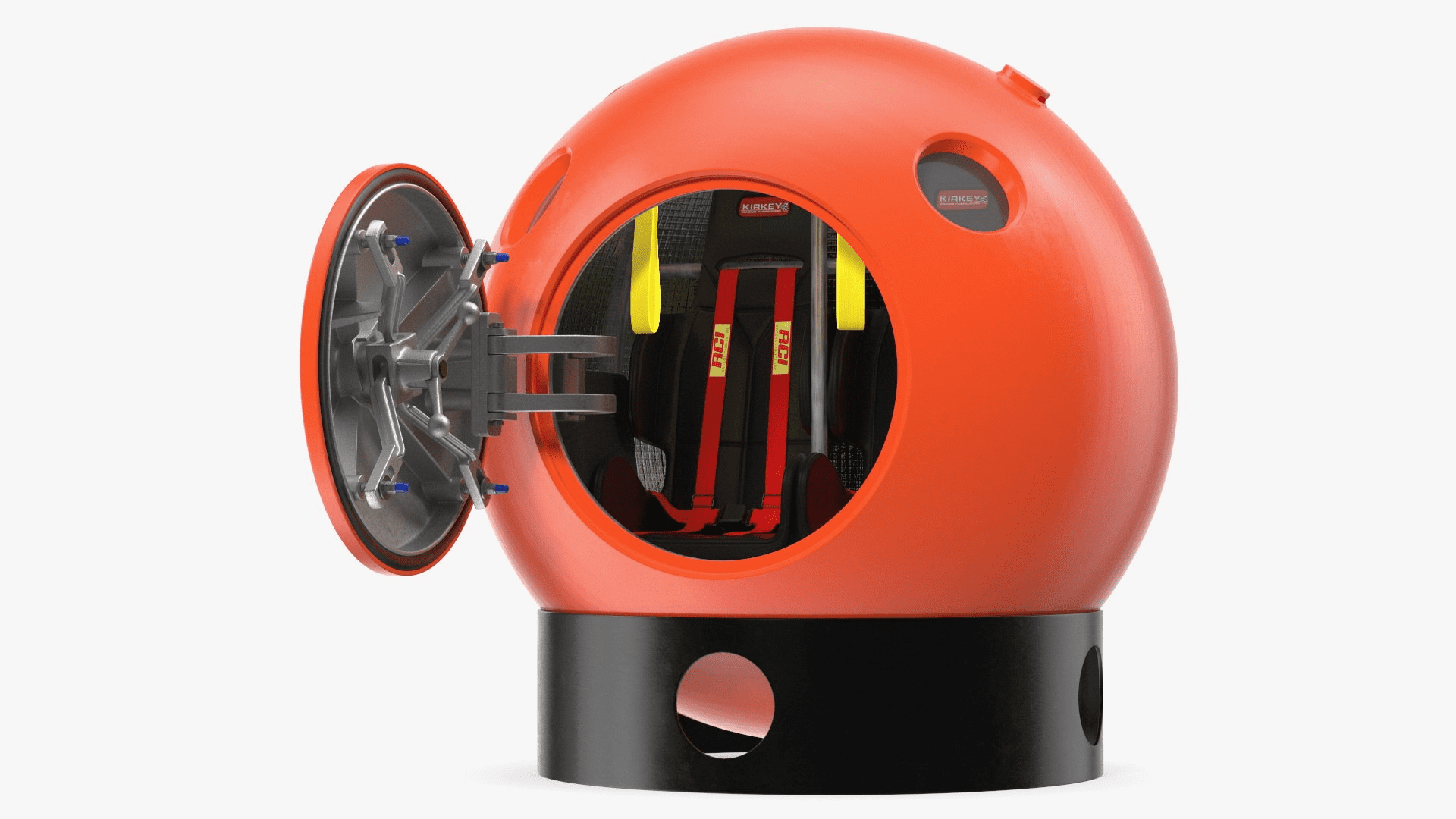 Image source: Turbosquid
Image source: Turbosquid
One example is this Tsunami Survival Capsule Rigged - a high-quality 3D model with a photorealistic presentation, modeled in 3ds Max 2014 and V-Ray. It features a fully-textured, detailed design for close-up renders without post-processing.
Creating a prototype of a project or new product saves time and effort compared to conceptualizing it from scratch. Using 3D Printing to create prototypes lets you determine which aspects of your tasks require adjustments or are unsuitable for the current project phase.
Here’s why 3D Printing is the top choice for creating product prototypes. It Is:
 Image source: ilopez3dmodels
Image source: ilopez3dmodels
Prototypes enhance product appeal and impress investors. 3D Printing offers affordability, ease, and quick market entry for various applications. You can prototype things like:
Depending on the product, you can print a functional prototype within hours, enabling you to test its performance and appearance, make improvements, and print new versions on the same day.
Handcrafted jewelry is known for its intricate details and time-consuming nature. But, it requires significant time, patience, and skill.
In contrast, 3D Printing offers a more affordable, efficient, and faster production method for professional jewelers, allowing them to create high-quality, distinctive jewelry. You can print intricate or geometrical designs of:
 Image Source: Septillion
Image Source: Septillion
The jewelry market has transformed with 3D Printing, offering customizable options for precious metals like gold and silver. 3D printing allows for unique, personalized creations in various materials.
Throughout history, humans have relied on tools to accomplish various tasks. From farmers to engineers to 3D printing enthusiasts, tools are essential. The exciting news is that they can 3D print their devices.
While it may not be possible to create functional hammers or wire cutters on a standard plastic 3D printer, there are surprising options for printing valuable tools. Here are a few examples:
 Image source: Selva
Image source: Selva
 Image source: cults3d
Image source: cults3d
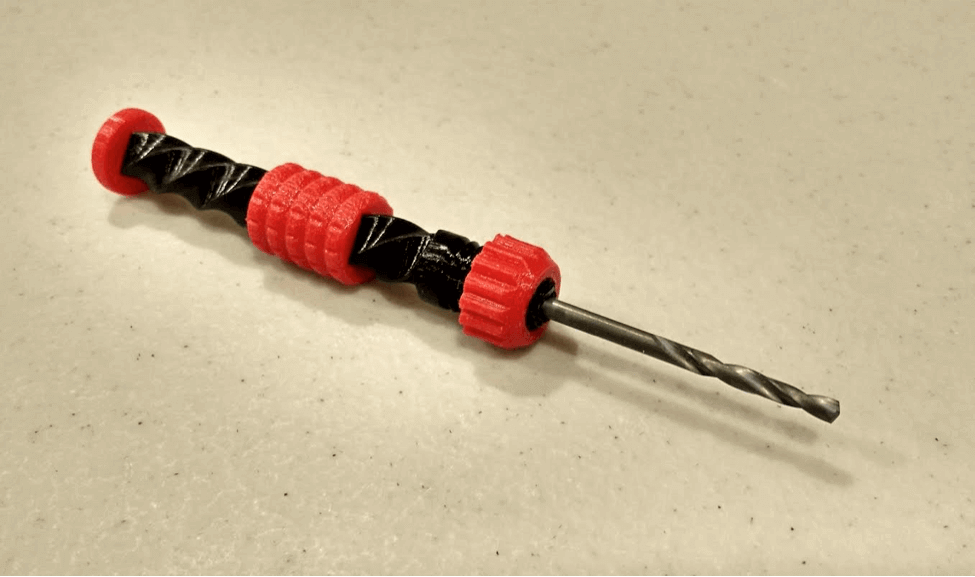 Image source: all3dp
Image source: all3dp
 Image source: instructables
Image source: instructables
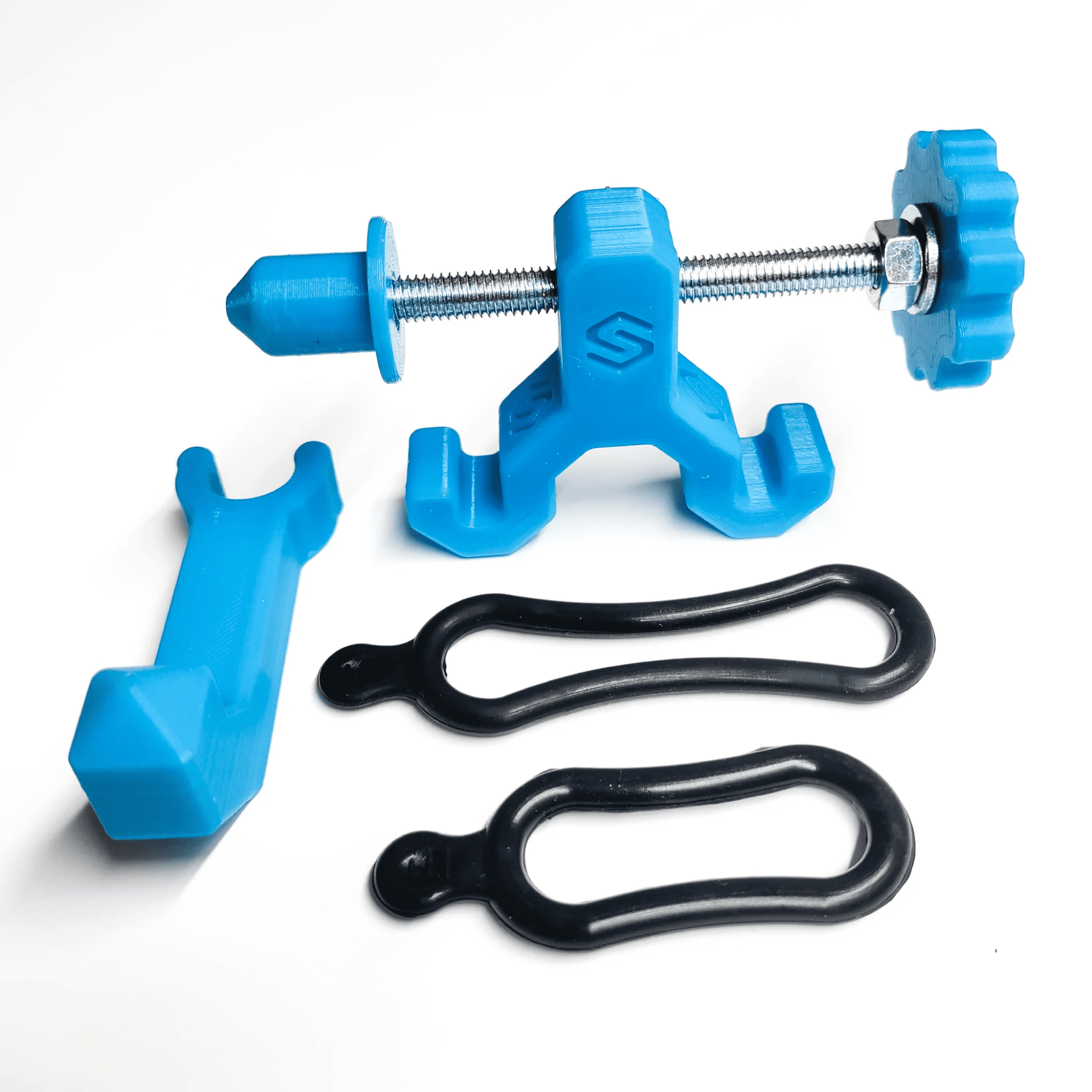 Image source: singletrackworld
Image source: singletrackworld
By 3D Printing these tools, individuals can access customized and valuable items that may not be readily available in local shops.
The struggle to provide adapted, high-quality amputee devices is a global challenge. Traditional prosthetics are often expensive and ill-suited to the specific needs of patients.
However, 3D Printing is significantly impacting the field of rehabilitative medicine, particularly in the realm of prosthetics.
 Image Source: Designwanted
Image Source: Designwanted
3D Printing presents a significant advantage for prosthetists, enabling them to develop customizable prostheses. They can craft 3D-printed prosthetic hands, functional wrists, and other tailored solutions with additive manufacturing.
This solution opens a realm of possibilities for engineers and researchers in prosthetics.
Toy production is significantly enhanced by 3D Printing, particularly in terms of customization. 3D Printing allows for rapidly producing toys with distinct shapes, designs, and colors.
Children can be rough with their toys, resulting in parts breaking or going missing. 3D-printed toys offer easy replacement of lost or damaged parts, saving parents time and money by reducing the need for traditional parts.
 Image Source: 3Dnatives
Image Source: 3Dnatives
A wide range of 3D-printed toys is available, including popular choices such as:
These examples showcase the versatility and creativity that 3D Printing brings to the world of toys. With the ability to customize designs and create unique pieces, 3D-printed toys offer endless possibilities for play and exploration.
Home decoration has become more straightforward and budget-friendly. You can now print charming vases for flowers, stylish living room lamps, and practical organizers to enhance your space.
 Image Source: Weburbanist
Image Source: Weburbanist
No matter your style, there are 3D prints available to suit your preferences. Here are some of the most extraordinary 3D-printed ideas for home decor.
 Image Source: cults3d
Image Source: cults3d
 Image Source: etsy
Image Source: etsy
 Image Source: 2bcreationsstore
Image Source: 2bcreationsstore
 Image Source: etsy
Image Source: etsy
The use of 3D Printing is widespread. Explore the industries benefitting from using 3D Printing in the next section.
The 3D Printing industry has grown significantly, with over $4.4 billion in 2013 to $21 billion in 2021. its remarkable progress is attributed to the increasing range of applications across various sectors.
Multiple industries, including healthcare, automotive, construction, and manufacturing, have been revolutionized by 3D printing. It enables the rapid and cost-effective printing of vital components, fostering advancements in numerous industries.
Let's delve deeper into the diverse industries benefiting from 3D Printing.
3D food printing is a revolutionary technology that is changing how we make and enjoy food. It allows us to create intricate shapes and designs, creating unique and exciting culinary experiences.
The innovative and eco-friendly method uses plant-based or lab-grown materials to reduce food waste and material usage. Overall, 3D printing is a sustainable alternative to traditional methods.
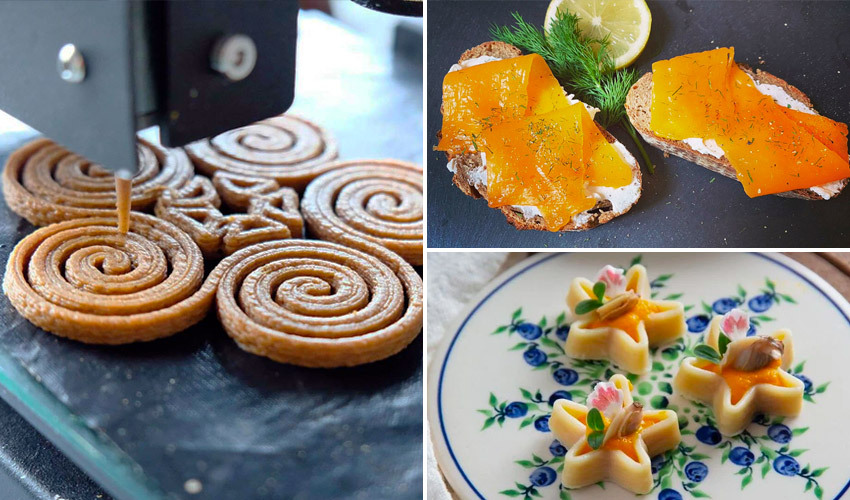 Image Source: 3dnatives
Image Source: 3dnatives
The process involves using a 3D printer with edible materials like dough, chocolate, or pureed fruits and vegetables as "ink" to create the desired food shape. It starts with a digital design, which the printer then brings to life layer by layer.
The medical field constantly seeks new technologies to enhance treatment, and 3D Printing is a perfect fit. Doctors, dentists, and pharmaceutical manufacturers are increasingly using 3D Printing for personalized healthcare solutions and improved organ substitutes.
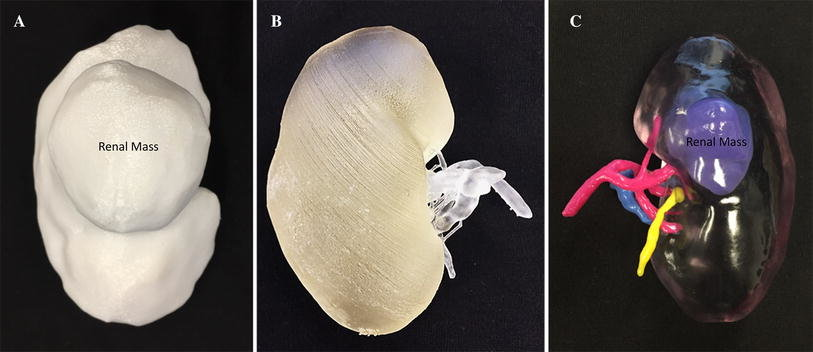 Image Source: Researchgate
Image Source: Researchgate
There are several areas in the medical field where 3D printing has benefits:
 Image Source: embodi3d
Image Source: embodi3d
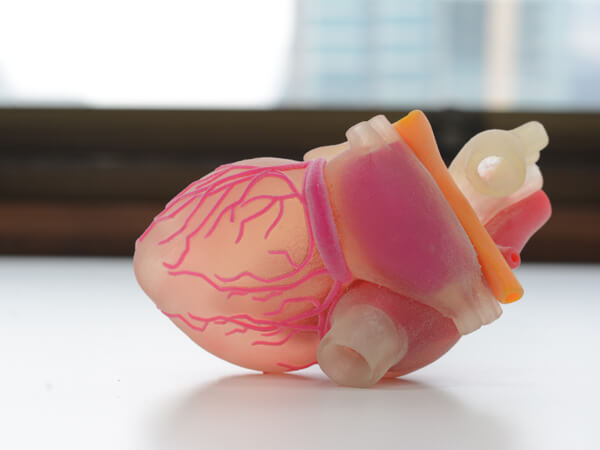 Image Source: nationalchildrenresearchcenter
Image Source: nationalchildrenresearchcenter
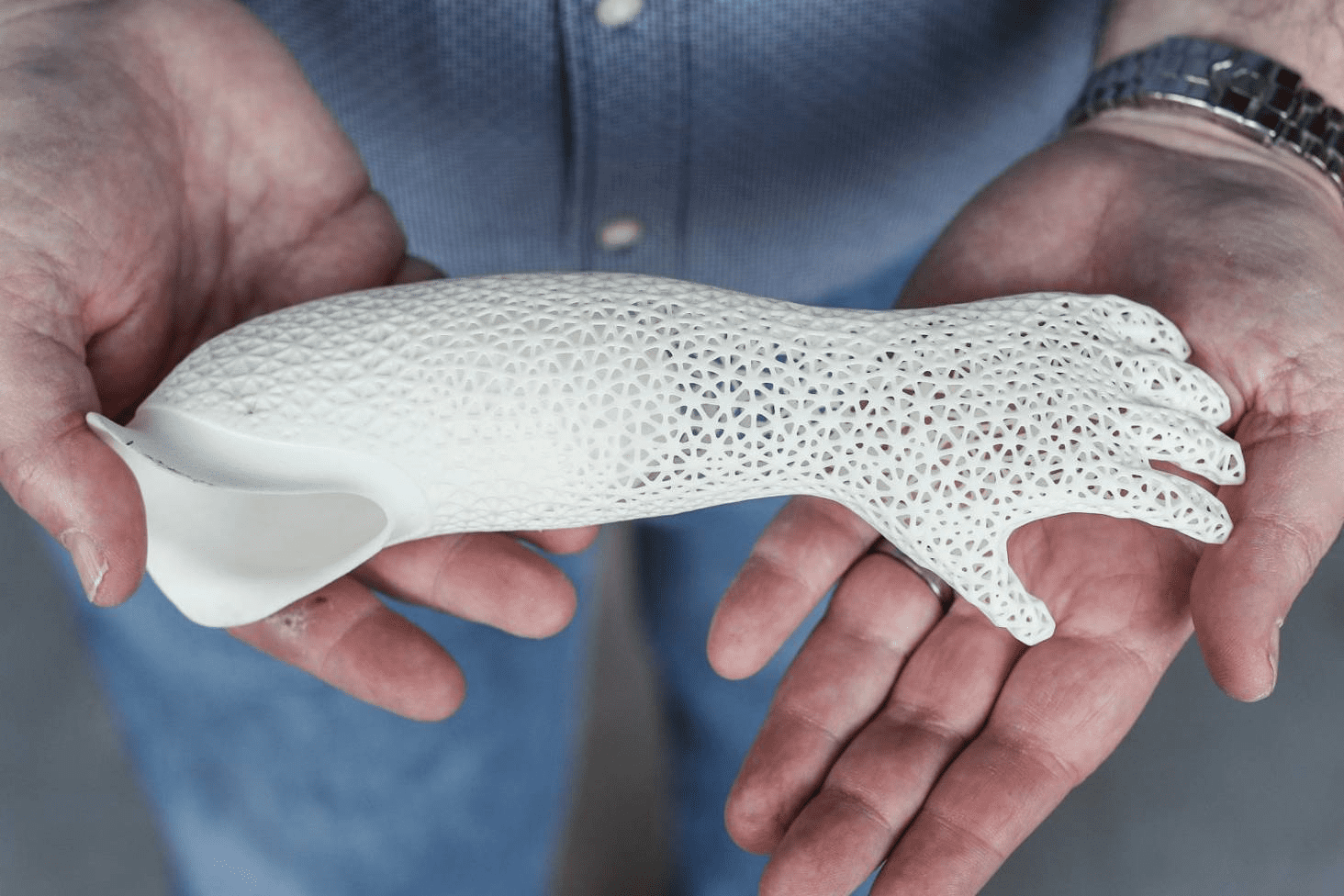 Image Source: stuffco
Image Source: stuffco
Overall, 3D Printing is revolutionizing the medical field by providing advanced tools for surgical planning, realistic organ modeling, and the development of customized body parts.
Integrating 3D Printing in education fosters creativity by enabling learners to transform their visions into tangible objects. Students can design and create physical items, like 3D-printed statues, to enhance their learning experience.
This technology improves problem-solving skills by allowing students to tackle complex math equations and explore scientific concepts. Educators can present real-world challenges, like climate change solutions, to encourage teamwork and develop essential skills.
 Image Source: 3dprint
Image Source: 3dprint
By embracing 3D Printing, students become responsible, confident, independent, and innovative professionals, well-prepared for the professional world.
3D Printing enables researchers and conservationists to create replicas of endangered species, study them without disturbance, and develop monitoring and protection tools.
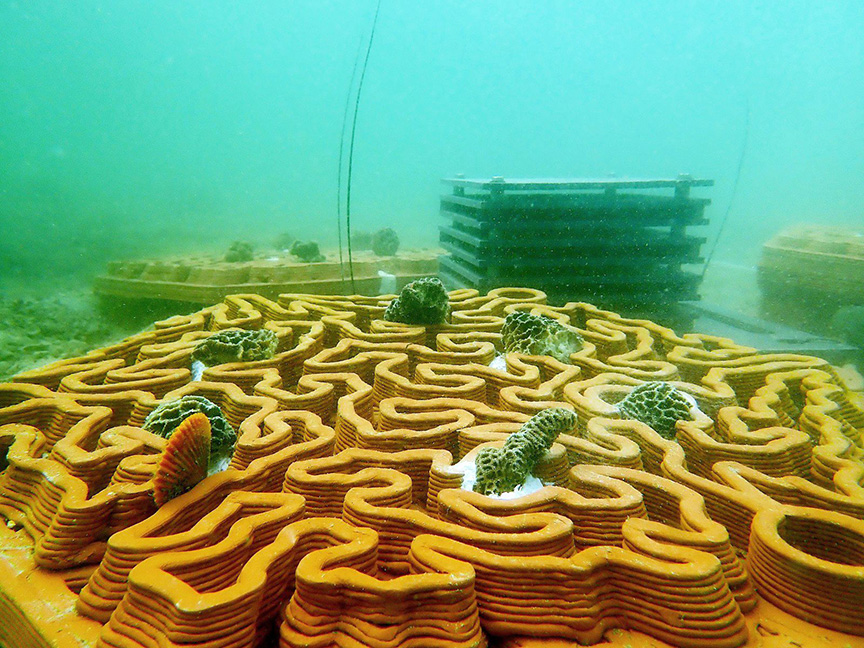 Image Source: 3dprinting
Image Source: 3dprinting
This technology benefits various industries and contributes to advancing wildlife conservation efforts. Furthermore, 3D Printing enables the creation of tailored artificial habitats and intricate burrows for different species, enhancing their well-being.
This technology opens new possibilities for effective conservation practices, promoting the preservation of wildlife and biodiversity for generations to come.
In the construction industry, 3D Printing is emerging as a transformative technology. Machines replace manual labor in constructing structures, offering cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, and faster completion times for houses and offices.
Moreover, the potential extends beyond buildings, including infrastructure components like
 Image Source: Reuters
Image Source: Reuters
In complex projects, construction companies can employ 3D Printing to create customized materials with precise measurements, reducing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Aerospace has been an early and enthusiastic user of 3D printing technology. They have found that 3D Printing allows them to create lightweight, complex structures that are both strong and stable.
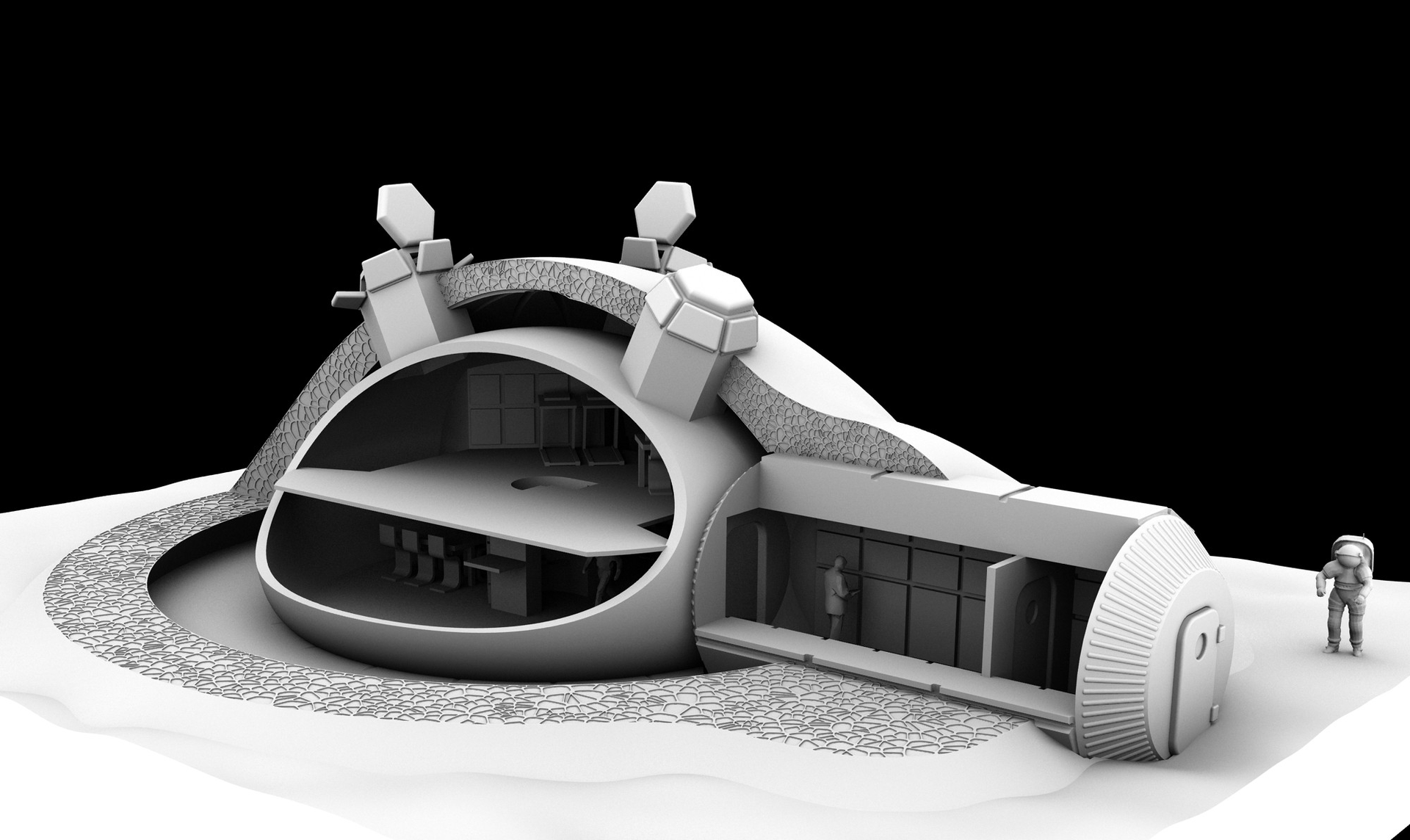 Image Source: ESA
Image Source: ESA
In aerospace, achieving lightweight designs while maintaining performance is crucial. 3D Printing enables the creation of intricate parts, enhancing efficiency through optimized designs. This technology has revolutionized aerospace by advancing component production and design.
The automotive industry has experienced significant advantages from integrating 3D printing technology. It offers cost-effective solutions by eliminating the need for extensive part storage and reducing production expenses, offering various personalization choices to automakers and drivers.
 Image Source: Automation
Image Source: Automation
Moreover, 3D Printing significantly reduces production time by minimizing material waste and allowing manufacturing innovation and flexibility.
With its transformative capabilities, 3D Printing has the potential to revolutionize vehicle production and customization in the automotive industry. This ability could lead to more efficient and personalized vehicles for consumers.
The film industry relies heavily on 3D print shops for various aspects of moviemaking, from special effects to creating movie sets. 3D-printed props have revolutionized the cinematic experience, allowing for endless possibilities and expanding the potential of special effects.
 Image Source: zishop
Image Source: zishop
This technology has become a significant attraction for moviegoers, with 3D printing used in a wide range of films, from animated movies to blockbuster hits. 3D printed costumes, props, and designs give characters life, enhancing the cinematic experience's realism.
Incorporating 3D Printing technology into the luxury fashion sector brings numerous advantages, including small batch sizes, efficient restocking, and improved fabrics for luxury brands. This advantage eliminates long overseas shipments, caters to exclusive brands, and ensures top-quality craftsmanship.
 Image Source: stratasy
Image Source: stratasy
The sustainability aspect of 3D Printing allows for easier recycling and reusing of clothing, addressing concerns raised by the fast-fashion industry. Advancements in technical capabilities and 3D Printing can transform production and commerce.
Here’s a video showing how designers use 3D Printing for a collection.
From design and prototyping to delivery time, 3D-printed clothes reshape the entire value chain in the garment industry, revolutionizing the fashion industry by:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern technology, 3D Printing has emerged as a game-changer with many advantages.
If you're interested in learning more about the advantages of 3D Printing, keep reading.
The advantages of 3D Printing technology include lighter parts, lower costs, and shorter lead times. It is primarily due to its enhanced design freedom. It also allows highly customized and unique geometries in part design.
The table below summarizes the advantages of using 3D Printing.
|
Advantages of using 3D Printing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The flexibility of 3D Printing, enabled by design freedom and a wide variety of materials, makes it a versatile solution for industrial manufacturing. This design versatility distinguishes 3D Printing, opening up new opportunities for intricate and customized creations.
3D Printing has revolutionized multiple industries with its versatility and potential. With this technology, anyone can easily create objects ranging from replacement parts and prototypes to jewelry, tools, and home decor.
Its applications span various sectors, including food, medicine, education, wildlife conservation, construction, aerospace, and automotive. The ability to customize, the cost-effectiveness, and the efficiency offered by 3D Printing have significantly advanced these fields.
The possibilities are endless when using 3D Printing, and its significance in various industries continues to grow. As technology progresses, we can expect even more innovative applications and exciting developments in the future.
Investing in a 3D printer is worth it if your project involves producing numerous prototypes. But if you want to explore 3D modeling, printing your designs with a 3D Printing service is more practical.
Potential risks include inhaling hazardous substances, skin exposure to harmful chemicals, fire hazards, and possibly burns due to high operating temperatures.
No. It is unsafe to leave a 3D printer unattended during Printing, as fires have erupted and spread in the vicinity.
The thin areas in 3D prints can be fragile and prone to breaking. Depending on where and how they are stored, 3D-printed PLA objects can last from one month to several decades. It can degrade at various rates depending on its surroundings.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 08, 2024
Updated · Feb 05, 2024



