
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Aug 18, 2023
Deyan is an avid enthusiast and self-proclaimed fan of the Windows operating system. His passion for... | See full bio
If I was asked to describe myself using just a few words, I’d go with digital marketing expert, ex... | See full bio
HDR, or High Dynamic Range, is a level of picture quality that boasts better color, clarity, and realism in images and videos. Unlike SDR (Standard Dynamic Range), HDR's sophisticated and adaptive technology enhances the contrast of the images. It preserves transparency
4K, or high-definition TV, adopts HDR screen technology, driving changes in television consumption, especially in streaming TV. This results in a vibrant and lifelike display, which producers, filmmakers, and developers want viewers to see.
Aside from TV screens, HDR has expanded to modern cameras, mobile phones, and computer monitors, enhancing photography and gaming experiences.
To better understand its function, this article will delve into all you need to know about HDR's benefits, types, and devices using it.
Key Takeaways
 |
Through metadata optimization, HDR enhances color, contrast, and realistic visuals in horror movies, nature documentaries, and video games. |
 |
The benefits of HDR as a screen technology include improving aspect ratio, color gamut, and vivid colors. |
 |
There are 5 HDR formats: HDR10, HDR10+, HLG, Dolby Vision, and Advanced HDR by Technicolor. All vary in features, specifications, and applications. |
 |
Various applications of HDR include better TV quality, a realistic gaming experience on a computer, and more improved mobile images. |
 |
The benefit of employing HDR as an imaging technique is that it captures a wide range of colors and details. |
HDR is a screen technology that improves monitors' display of colors and contrasts. This quality produces realistic visuals in horror movies, nature documentaries, and video games. Major game graphics support HDR for detailed, vivid visuals in dark settings.
Some games that have HDR include:
As a visual technology, it gained popularity in video games due to public demand for high-quality visuals. Besides video games, TV and movie enthusiasts prefer HDR over SD for entertainment.
Read on to learn more about HDR and how it works as a screen technology on different devices.
HDR operates through the metadata of an HDR TV or devices across different scenes. It optimizes contrast and brightness, introducing a wide color gamut (WCG). This optimization enhances TV, videos, and image quality by increasing image color range and depth.
|
📚Definition: HDR metadata enhances display device content by mastering properties and mapping content based on color gamut, a range of colors within the spectrum of colors, and peak brightness. |
Metadata can be static or dynamic - with static content remaining constant throughout a movie or scene. On the other hand, dynamic HDR content can change between sets and frames, depending on the mastered HDR format.
|
📚Static Metedata Definition: Static metadata, standardized by SMPTE ST 2086, contains content information. In contrast, Dynamic metadata changes throughout a clip, requiring a unique access process in diverse formats. |
Here’s a video presentation to further understand static and dynamic metadata.
|
|
HDR monitors significantly improve visual, with modern games and television embracing HDR technology. It also offers enhanced color support, such as 10-bit, for smoother hue transitions.
Using increased brightness and black Level HDR monitors improve the following:
|
✅ Pro Tip: To experience HDR video quality fully, you need an HDR-compatible display. It's also better to have an HDR source, such as a Blu-ray player, video streaming service, a game console, or a PC. |
HDR has many advantageous features. Some additional advantages of HDR are as follows.

HDR enhances the immersive experience by utilizing Wide Color Gamut for accurate display color range and realistic contrast. Higher brightness also leads to:
HDR enables a more enjoyable viewing experience with vivid, brighter, and lifelike images. This technology allows more detailed shadows and highlights, making images appear three-dimensional and realistic.

Additionally, a wider color gamut ensures more accurate colors, delivering natural and lifelike pictures with more precise representations and vivid details on-screen.

HDR offers an improved contrast ratio, enhancing vibrant and realistic imagery with enhanced details in bright and dark areas. This innovative technology provides the following:
The following section will delve into the formats of HDR, where HDR is used, and how each structure varies in application compatibility.
HDR is a spectrum - not a precise number like resolution or refresh rate. This causes varying qualities depending on the device used to view it.
There are numerous HDR formats, but the following are the most commonly encountered:
It is an open-source HDR format developed by the Consumer Technology Association. Although it is the most common HDR format supported by TVs, it is also the most limited. It uses static metadata and is incompatible with non-HDR televisions.
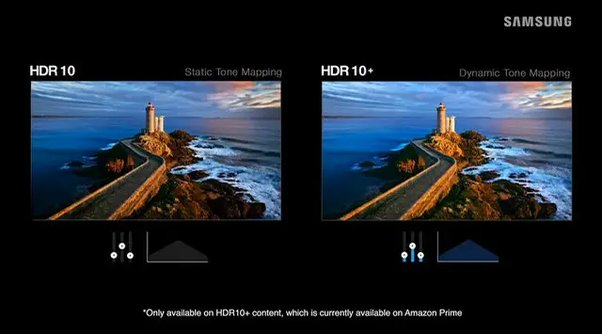
This is a more recent dynamic tone-mapping format found on certain TCL televisions manufactured in North America. It has a limited but expanding availability of HDR10+ content.
Here’s a video representing HDR10+ on mobile phones with its Qualcomm snapdragon.
|
✅ Pro Tip: Samsung introduced HDR10+, a free alternative to Dolby Vision. It enhances HDR10 information with dynamic metadata. It is mainly used on Samsung TVs and other brands. |
This HDR format is backward compatible and developed by Japan's NHK and Britain's BBC for cable broadcast scenarios. It is designed specifically for live broadcasts.
HLG ensures compatibility with existing TVs that do not support HDR. It is more prevalent in Europe, where HDR broadcast is near mainstream adoption.

A Dolby Laboratories-developed HDR standard. This format is less prevalent than HDR10 because a licensing fee typically requires a higher-end display.
This platform supports up to 10,000 nits of brightness, significantly higher than most current televisions and monitors. Here’s a short video representing Dolby Vision Demo 5.1.
This format aims to protect and enhance investments in legacy infrastructure and devices. Unlike static mathematical mapping functions, Advanced HDR uses real-time adaptive solutions.
It provides viewers with a visually satisfying experience for live events, including live-action sports, that matches the quality of offline post-production solutions blockbuster filmmakers use.

The table below summarizes the specifications and features of the five different platforms of HDR.
|
Features |
HDR10 |
HDR10+ |
HILG |
Dolby Vision |
AHDR |
|
Resolution |
4k |
8k |
- |
8k |
- |
|
HDR Type |
Static |
Dynamic |
Dynamic |
Dynamic |
Dynamic |
|
Peak Brightness |
1-4k Nits |
1-4k Nits |
1k Nits |
10k Nits |
- |
|
Bit Depth |
10 Bit |
10 Bit |
10 Bit |
12 Bit |
10 Bit |
|
Platform Availability |
Compatible with any platform |
Doesn’t support Netflix Vudu Apple 4k |
BBC |
Don’t support NVIDIA |
No platform available |
|
Content Availability |
Great |
Good |
Scanty |
Good |
None |
|
Backward Compatibility |
None |
None |
Full Support |
None |
None |
|
Price Range |
$299.99 |
$299.99 |
- |
$2,198-$2,799 |
- |
To fully visualize the different of HDR formats and contents, view the video below:
Now that you know the different types of HDR, find out which devices use these features in the following section.
HDR can boost image and video quality and enhance it for better results. Here are the different devices that use the HDR feature to give you a better experience.
HDR technology enhances the contrast between dark and light colors on TV screens, accurately representing reality.

This technology lets the eye perceive more detail, color, and light than typical televisions. It also gives you a clearer perception of horror movies and sun-filled scenes.
HDR video games provide a detailed and immersive gaming experience on Windows PC due to their expanded color range and luminosity.
Look at how HDR works on Assassin’s Creed Origins, one of Ubisoft’s first few games that adopted HDR technology.
Auto HDR increases color range and brightness to HDR, enabling users to play older titles with HDR on their HDR-capable display. This feature is accessible in more recent HDR-capable titles, such as DirectX 11 or 12.
Mobile HDR has evolved since 2017, with major manufacturers like Apple and Samsung offering flagship phones with HDR10, HDR10+, and DolbyVision standards.
These technologies enable advances such as:

|
✅Helpful Articles: To know more about HDR quality videos, check out Techjury’s articles on: |
HDR is not only used as a screen technology but also as an imaging Technique. Here's how it works.
The main benefit of HDR is that you can take a high-definition photograph of a picture with all the details in high-lighted and low-light areas.
Professor Mann developed the global HDR method in 1998, aiming to create images with:
This graphic detail contrasts images that usually can be against light or overexposed, burning the background completely. Here's how HDR is used in Photography.
|
🎉Fun Fact: Steve Mann is also coined as the father of wearable technology as he created the first smartwatch. His other creations include Smart Glasses and the Telepointer. |
The human eye perceives outdoor and indoor scenes differently than professional digital cameras and lenses. It adjusts for harsher light, rendering colors and detail more accurately than raw files.

HDR technology produces crisp images with excellent detail and lighting control, protecting against harsh sunlight and contrast views.
HDR is a powerful tool for photographers, enabling stunning highlights and shadows in images. With numerous programs available, choosing the most reliable one is tricky.
Here are the top choices for the best HDR software on the market:
HDR significantly impacted image quality due to its broad spectrum of supported platforms. It can sometimes be more readily apparent than other image metrics, such as resolution.
As it becomes the standard, display technology will continue to advance, and color accuracy and contrast ratio spectrums will continue to expand.
Yes. HDR is better than 4K on any screen size, thanks to HDR's enhanced color creation and contrast.
HDR camera settings should be used when you have trouble balancing light in landscape photography, revealing sun and shadow details. Avoid them for motion capture in sports photography.
The system must adhere to the HDMI 2.0a specification for delivering HDR content with static metadata (SMPTE ST 2086). HDMI is an interface that transfers UHD-1 and UHD-2 content to consumer displays.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 08, 2024
Updated · Feb 05, 2024



