
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Aug 07, 2023
Raj Vardhman is a tech expert and the Chief Tech Strategist at TechJury.net, where he leads the rese... | See full bio
Florence is a dedicated wordsmith on a mission to make technology-related topics easy-to-understand.... | See full bio
Emily Isla is an accomplished and dynamic professional, known for her exceptional leadership and exp... | See full bio
VMware technologies are a collection of software and solutions that lets you run numerous operating systems(OS)—or "virtual machines"—on a single piece of hardware.
It offers cloud-based software and virtualization solutions to its 500,000 customers worldwide to facilitate digital innovation and safeguard businesses' data.
In VMware server virtualization, a hypervisor is placed on the physical server to operate many virtual machines (VMs) simultaneously.
As each virtual machine can run its own OS, a single physical server can host numerous OSes simultaneously.
Read this article to learn more about VMware, its products and alternatives, and how it can benefit you and your business.
Key Takeaways
|
|
Virtualization from VMWare offers software-based simulation, platform-independent development environments, and resource sharing. |
|
|
|
VMware is divided into eight products and five applications. All have varying purposes in the system where it’s installed and applied. |
|
|
|
Enterprises benefit from VMware's low costs, redundancy, scalability, adaptability, and multiple OS support in cloud applications. |
|
|
|
Despite its advantages, VMware needs more efficiency in certain features, unfriendly software, compatibility, problem-solving, and dependability. |
|
|
|
Five other softwares offer similar features for users looking for alternatives to VMware, depending on what users or an enterprise needs. |
A virtual machine (VM) is the fundamental building block of VMware virtualization. A visitor operating system is a software-based simulation of a physical computer running in a virtual machine.
VMware offers a variety of file management utilities, including vSphere Client. This command-line interface for virtual machine administration enables the configuration of virtual machine parameters.
Users can choose from two types of Virtual machines—process VMs and system VMs:
Provides a platform-independent development environment by masking the hardware or operating system details, allowing a single process to act as an application on a host machine.
Example: Java Virtual Machine allowing Java programs to run on any OS.
Completely virtualizes to replace a physical machine. A system platform enables sharing of material resources of a host computer among multiple virtual machines, each of which runs its copy of the operating system.
Example: Utilizes a hypervisor, which can operate on isolated hardware, such as VMware ESXi, or on top of an operating system.
Learn the different products of VMware and how it functions through the following details.
VMware provides vast software and hardware, enabling robust cloud computing and virtualization infrastructure.
Many different products cover—depending on your requirements—apps, the cloud, networking, workspace, security, and more.
Find out what these VMware products are and how they manage your IT infrastructure through the following details.
A hypervisor, a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), allows a server to host numerous virtual machines and operating systems.
A "host machine" is the server where the hypervisor runs one or more virtual computers. On the other hand, a "guest machine" refers to each VM.
Hypervisors are responsible for isolating the virtual machine's resources from the hardware system and distributing them appropriately.
Using hypervisors reduces hardware costs and improves cloud accessibility and scalability, enabling cloud migration.

There are two types of Hypervisors - Bare-metal or Native Hypervisors and Hosted or Client hypervisors. Their functionality and examples are stated in the table below.
|
Bare-metal or Native Hypervisors |
Hosted or Client hypervisors |
|
|
Functionality |
|
|
|
Examples: |
|
|
VMware vSphere is VMware's enterprise virtualization platform, which includes the ESXi hypervisor software and the vCenter Server management platform for administering multiple hypervisors.
It supports the power of virtualization to transform data centers into simplified cloud computing infrastructures, allowing IT organizations to provide flexible and dependable IT services.
VSphere is available in
Each supports policy-driven storage of virtual machines, live workload migration, and integrated security features.
|
Features |
Standard |
Enterprise |
Platinum |
|
Policy-driven storage |
|||
|
Live workload migration |
|||
|
Integrated security |
|||
|
VM-level encryption |
|||
|
Integrated container management |
|||
|
Load balancing |
|||
|
Centralized network administration |
|||
|
Automated security threat responses |
|||
|
Third-party security operations tools. |
vCenter Server is an essential vSphere management component. It enables the management of virtual machine deployments across many host servers.
Powered by VMware's Photon OS, vCenter Server eliminates the need for third-party updates or upgrades. It allocates resources to virtual devices, monitors performance, and automates workflow. This instrument can manage user privileges under an individual user's policies.
VCenter Server consists of three principal components:
VMware Tanzu offers comprehensive capabilities for modernizing your applications and infrastructure to deliver improved software for production perpetually.
Its portfolio simplifies multi-cloud operations and gives developers simple access to the necessary resources.
The VMware Tanzu for Kubernetes Operations package enables platform operators to construct, administer, and monitor Kubernetes environments across multiple on-premises and public cloud platforms. The platform also allows developers to;
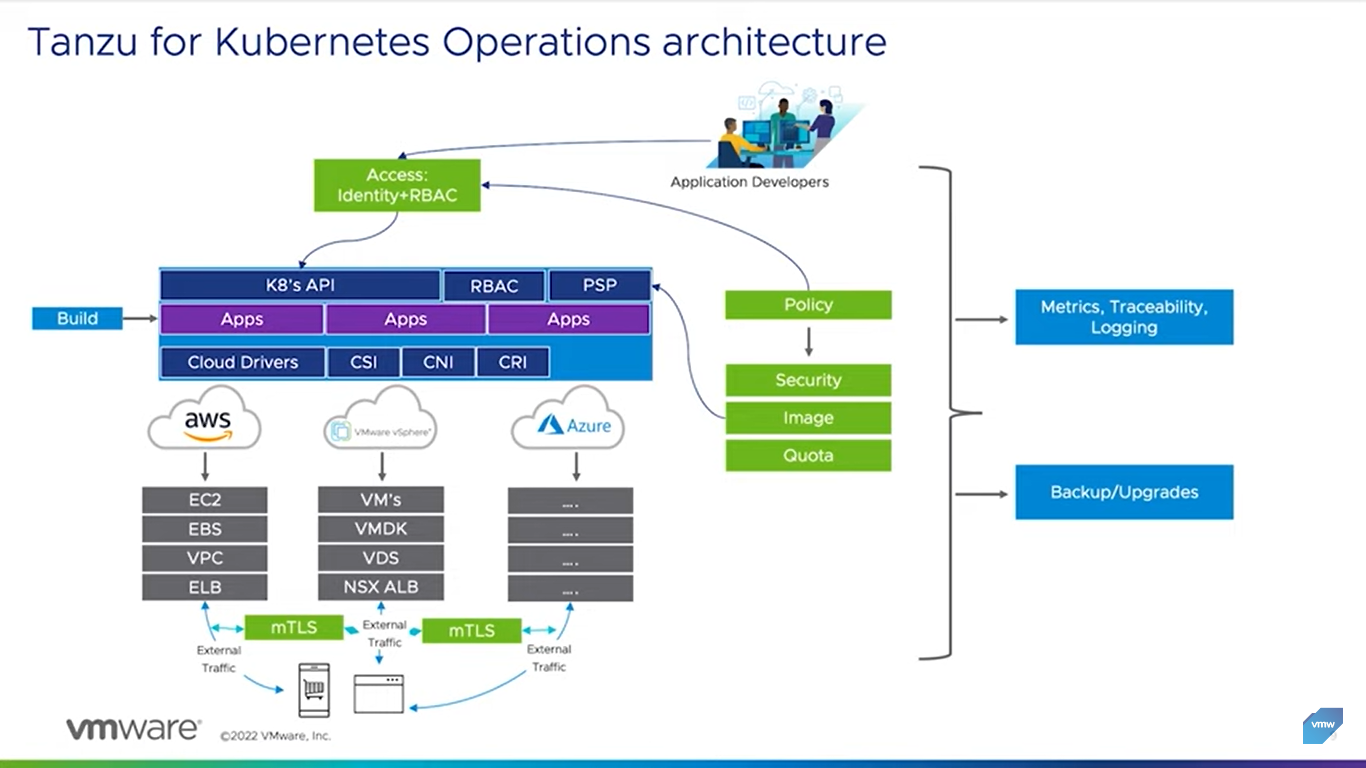 Source: VMware
Source: VMware
With VMware Virtual SAN, a single virtualized x86 server may act as a hyper-converged infrastructure node, providing the following;
By aggregating server-attached flash devices and hard disk drives (HDDs), virtual SAN delivers high-performance, highly dependable shared storage.
Virtual SAN offers predictable scalability and all-flash performance at a fraction of the cost of purpose-built storage arrays.
Like vSphere, Virtual SAN lets users choose from a wide range of hardware and deploy and manage it for different IT workloads and use cases.
Cloud Management is the monitoring and optimization of the utilization of one or more private or public clouds. Typically, organizations use a cloud management platform to oversee cloud usage.
Cloud administration enables IT administrators to distribute workloads across multiple clouds and control the cost of cloud resources.
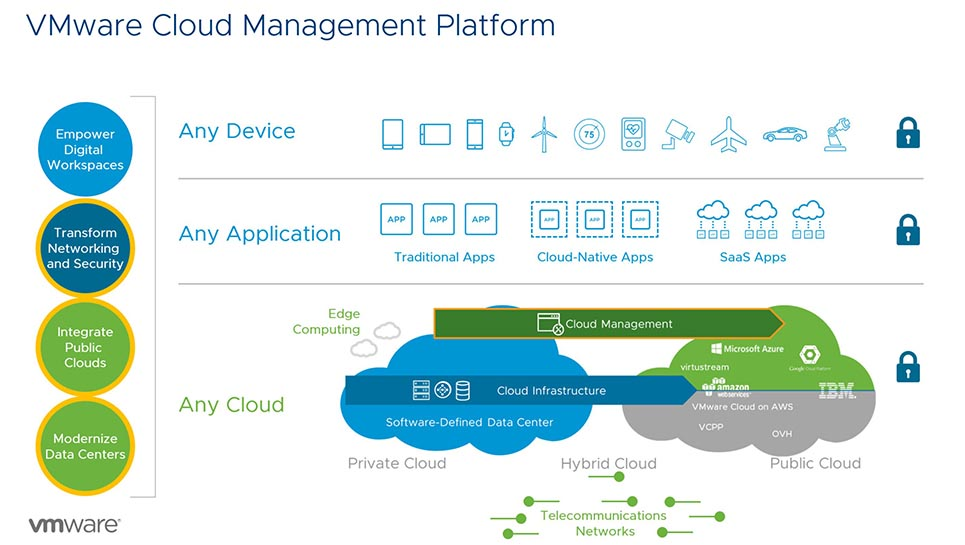
Source: VMware
Cloud management platforms may manage data, content, or applications in the cloud or all three. These are:
The VMware NSX network virtualization platform enables the creation of secure virtual networks on top of an existing physical network and virtual server infrastructure.
NSX utilizes Software-Defined Networking (SDN) to programmatically define virtual networks on demand, regardless of the underlying hardware in your infrastructure.
When you need to increase the capacity of your network, you can configure a second virtual network or reconfigure an existing one instead of purchasing additional hardware.
Furthermore, VMWare NSX provides the following features and benefits:
VMware Workspace ONE is a platform that transmits and manages any application on any device by integrating the following,
Using code, network infrastructure may be deployed and configured automatically, and it can be expanded to include virtual components.
For the following section, learn and investigate various products' platform implementation and networking across multiple systems.
A virtual machine is a computer file, also known as an image, that mimics the behavior of physical hardware.
It's common for people to utilize virtual machines at work, where each user has an isolated computing environment to accomplish things like running a different OS or even just conducting all of their jobs.

Source: VMware.
Read the following to learn more about the cross-cloud services of VMware and its applications.
Using the software, a virtual network connects machines and devices regardless of location. Physical switches and routers perform OSI model functions in physical networks, including network interface devices (NIC).
Virtual networking simplifies network management by centralizing and streamlining access to dispersed components, making it more affordable and efficient.
Multi-cloud architectures improve service delivery, reduce costs and business risk. This enables innovation and freedom for business and IT lines to utilize diverse cloud providers without lock-in.
Across all industries, organizations are embracing multi-cloud to:

App Platform - Ensuring Cloud-Native App Development
VMware covers you if you need to develop and manage many applications. Thanks to VMware's multi-cloud Kubernetes platform, you can construct, secure, and instantaneously modernize apps and run them across any cloud.
This platform is characterized by its consistency and stability. It ensures cloud-native app development, modern protocol adherence, and straightforward app updates.
VMware Anywhere Workspace provides solutions to facilitate today's mobile workforce. A platform that prioritizes employees provides secure, frictionless experiences for all work styles.
Anywhere Workspace combines market-leading end-user computing technologies to provide
It combines market-leading Unified Endpoint Management, Virtual Apps & Desktops, Workspace Security, and Digital Employee Experience technologies to provide IT and employees with a single, seamless, and secure experience.
VMware Anywhere Workspace consequently empowers highly engaged employees and reduces silos, disparate tools, and operational overhead.
VMware aids in ransomware defense by strengthening systems. It finds and evicts threats with strong lateral security in private, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments.
Additionally, VMware provides network security, regardless of the complexity of your environment.
Vmware secures data through the following:
For the next part, discover some of the benefits of using VMware.
VMware has numerous advantages, as evidenced by its many products that aid in security, networking, storage, and other areas.
Here are the benefits of using VMware.
The low costs of WMware enable an affordable, software-based virtualization platform for cloud computing solutions, making it accessible to large businesses and all users.
Adding and removing virtual machines is easy on VMware. It offers quick rollback data recovery methods for restoring modified or deleted files in case of data loss or corruption.
VMware is ideal for businesses requiring multiple virtual machines, as it simplifies adding and implementing them efficiently through straightforward steps.
Secure testing of applications is possible on VMware. This allows users to test updates and patches before installing them on a tangible computer. It also helps prevent malware and unreliable software usage.
In VMware, a single server can administer multiple operating systems. This configuration ensures superior resource management. Moreover, users may access each of the operating systems simultaneously.
Now that you know VMware's benefits, knowing any disadvantages is crucial. You can read it in the following section.
There's no denying the benefits that VMware offers in the workplace. But it doesn't mean there aren't any problems with this program.
The following details show the drawbacks of using VMware:
VMware can only deliver optimal performance on systems with premium devices. Therefore, attaining the desired performance with lower configuration systems is impossible.
Also, the software is wholly dependent on your system's resources. Predicting how your design will perform with the current resources takes a lot of work.
VMware needs to be more user-friendly. Operating the software requires technical expertise and time to study, but numerous online tutorials are available for further learning.
VMware's dependability is a concern due to its tangible devices, which must provide equivalent performance to avoid additional issues and make it impossible to predict its dependability.
VMware requires specific hardware requirements for optimal deployment, including a 64-bit x86 processor, 4GB RAM, and 1GB Ethernet controller. Please meet these requirements to ensure sufficient system efficacy.
Virtualized systems differ from conventional workstations, making troubleshooting challenging and requiring additional effort compared to physical systems. This makes determining root issues difficult.
If you have problems utilizing the VMware software, here are alternatives that you can use.
These VMware alternatives are the most frequently mentioned by users and reviewers. Before selecting a Virtual workstation, one should consider the following fundamental and essential features.
The table below showcases different VMware alternatives and their advantages when used.
|
VMware Alternative |
Features |
|
1. V2 Cloud  |
|
|
2. Azure VM  |
|
|
3. Virtual Box  |
|
|
4. IBM PowerVM  |
|
|
5. Virtuozzo  |
|
VMware for novices is a straightforward method for creating and running virtual machines on desktops and laptops.
Despite being simple to use, VMware products require expertise in servers, networking, cloud, and applications for enterprise environments.
VMware's cloud computing and computer system virtualization solutions are cutting-edge and versatile. They provide the infrastructure and management tools for your next-generation applications while rapidly bringing the older ones up to date.
The platform's performance, efficacy, and security are commendable when aggregating and virtualizing physical servers for limitless applications. It is the optimal foundation for any size cloud environment.
VMware server virtualization is a method used for turning a single physical server into a group of virtual servers that operate as their own. Each functions as a VMware virtual machine but essentially shares the resources of the main machine.
Moreover, each virtual machine can run its own VMware operating system. VMware virtualization uses a hypervisor to create a virtual environment—efficiently distributing RAM and other resources across various virtual machines.
VMware supports a hypervisor to run containerized workloads in a Kubernetes cluster. The solution is ideal for users who want to separate each VMware virtual platform for different projects and other purposes.
So what is VMware used for? Although the VMware platform creates virtual machines and cloud computing solutions, it can be used for several applications. Key benefits include enabling seamless scalability, network flexibility, automated operations, remote workforces, and better security—all of which businesses can use to cut costs.
What does VMware do? In simple terms, it takes a single computer and creates multiple virtual computers that share the original’s resources.
Imagine that your desktop Windows PC uses VMware on a single home-user basis. You could operate two or three other Windows environments, which function like two or three separate PCs. The only difference is that they’re reliant on the underlying hardware of the original physical system.
No. VMware is not commonly considered an operating system. But with virtualization, VMware hypervisor users can install multiple operating systems—one for each virtual server. These include various OS options—from Windows Vista to Windows 10, alongside Windows Server editions 2007 SP2. There are also options for CentOS, Linux, and Ubuntu for those who shun Microsoft.
And vSphere (formerly VMware ESXi)—based on the VMkernel operating system—is a hypervisor that functions on the machine without requiring any other standard or VMware operating systems.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 08, 2024
Updated · Feb 05, 2024



