Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Aug 17, 2023
Nero is an all-around wordsmith with a degree in Communication Arts— not the vicious emperor you m... | See full bio
Florence is a dedicated wordsmith on a mission to make technology-related topics easy-to-understand.... | See full bio
An equalizer (an EQ) is an audio tool that boosts, lowers, or neutralizes specific audio frequencies. It enables you to adjust the audio output to emphasize particular frequencies over others.
However, adjusting the equalizer requires an understanding of how it works. Finding the best equalizer settings allows you to achieve the best sound quality and immersive listening experience.
In this article, you will read about the best equalizer settings for different devices or activities and get some tips for setting frequencies. Let's dive in!
🔑Key Takeaways
|
An equalizer is a piece of audio equipment that isolates frequencies and either boosts, cuts, reduces or leaves them as they are. |
|
|
Frequency ranges are categorized into bass (low frequencies), mid (mid frequencies), and treble (high frequencies) |
|
|
Each frequency range has a significant impact on the overall sound profile. |
|
|
Many devices include genre-specific presets that you can use as a starting point and then fine-tune. |
|
|
There is no one-size-fits-all solution for the best equalizer settings, as you can adjust frequencies based on your preferences. |
The music you listened to may have sounded good, but you can always make it sound much better with an equalizer.
EQ allows you to tailor the music to your liking by choosing frequencies you want to boost and those you want to weaken. It lets you adjust your frequencies to focus on the song's elements.
The following sections will cover frequency ranges, the best equalizer settings, and some tips on adjusting your equalizer.
|
📝Note: An equalizer can make considerable improvements to your audio. However, it also helps to consider other factors that impact your audio quality. |
Frequency is the number of cycles per second of the sound wave. It is about how high or low the sound is. When you listen to music or sound, it can be high or low. Frequency in audio is how fast or slow the sound waves are moving.
The next section covers seven different frequency ranges to help you understand how an equalizer works.
Frequency ranges (or bands) are defined as a collection of frequencies ranging from lower to higher frequencies.
The commonly referenced frequency range is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, and people can hear less than this entire range as they age.
Here is the breakdown of seven frequency ranges:
The sub-bass range is the lowest sound audible to humans. They produce a powerful, deep low-end sound typically reserved for bass guitars, kick drums, and low synthesizers.
This frequency range is felt more than heard, like when the bass drops at a live show, and you feel it in your chest. They bring warmth and impact to audio experiences.
The bass range is what many people are passionate about. These frequencies are responsible for creating the foundation and depth of sound.
Bass is an essential element in various music genres, providing rhythm and adding richness to the audio experience.
To some extent, most musical instruments are in this range, so finding a balance between them is critical.
When too much happens in this range, instruments can sound muffled or boxy. When there is less, it will sound empty or hallowed.
The mid or midrange contains many fundamental frequencies in musical instruments and the human voice. It is the most audible range for humans.
In audio production and mixing, the midrange is essential for achieving clarity and presence in the sound. Balancing the mids properly can create a well-defined soundstage.
The upper mids frequency range is where human ears are the most sensitive. It is seldom boosted, as it can cause damage to the ears if made too loud.
Boosting too much in the upper mids can cause the track to sound harsh or edgy or exaggerate sibilance in vocals. This can be hard to mix because the vocals, guitars, and drums compete for attention in a small space.
|
✅Pro Tip: When in doubt, stick with the vocal and boost a different range of frequencies on the other tracks. |
The presence range determines the clarity and definition of a sound. It is the frequency range in which most home stereos center their treble control.
Music in this range is well-balanced, adding warmth and sweetness to high strings, synthesizers, and orchestral music.
|
✅Pro Tip: Overboosting in this range will cause an irritatingly harsh sound, and cutting in this range makes the sound more distant and transparent. |
They are known as brilliance or air because the only frequencies this high are harmonics that appear to sparkle.
These frequencies are the highest that the human ear can perceive. They range from stinging and irritating to ambient and atmospheric.
Here’s a table summary of the seven different frequency ranges, including their simplified and subjective terms:
|
Frequency Subset |
Frequency Values |
Simplified Term |
Subjective Terms |
Description |
|
Sub-bass |
20 to 60 Hz |
Bass |
Lows |
This is the low musical range. Includes upright bass, bass guitar, and tuba |
|
Bass |
60 to 250 Hz |
Normal range of human vocals |
||
|
Lower Mids |
250 to 500 Hz |
Mids |
Mids |
Brass instruments and mid instruments, such as the alto saxophone and clarinet, are found here |
|
Mid |
500 to 2000 Hz |
The most audible range for humans Instruments such as the violin and piccolo can be found here |
||
|
Higher Mids |
2000 to 4000 Hz |
Human ears are sensitive in this frequency range. Here, you can find trumpets that are four times louder |
||
|
Presence |
4000 to 6000 Hz |
Highs |
Treble or Highs |
Harmonics for violence and piccolo are found here. |
|
Brilliance |
6000 to 20000 Hz |
Sound becomes more like whines and whistles, and cymbals are found here. |
Continue reading to find out what the best equalizer settings are for the different audio devices you have in the next section.
Whether you are a casual listener, audiophile, or music professional, mastering equalizer settings can improve your music experience.
The equalizer allows you to adjust the balance of frequencies finely and is the key to unlocking the true potential of any audio setup.
Here are the best equalizer settings:
Bass is not a music genre, but many people are looking into getting more bass, regardless of the music they listen to.
Listening to music with a woofing quality can add a sense of energy and excitement. The best equalizer for bass sound should look like this:
 Image source: Play the Tunes
Image source: Play the Tunes
You may raise the sub-bass lever on the extreme side of your equalizer and push it halfway to the top of the volume. Place the bass frequency lever at a slightly lower level and keep all other levels lined up descendingly.
|
✅Pro tip: Consider your speaker's size and capacity before changing your equalizer. Make sure they work with your equalizer. |
An equalizer is truly indispensable when it comes to voice recording. Equalizers can make your voice recording darker or brighter, smoother or crisper, dull or sparkly, light and airy, or any other creative combination.
Here’s an ideal equalizer setting for voice recording:
 Image Source: TechJury
Image Source: TechJury
To bring clarity, you must optimize EQ for human speech. Frequencies can differ between the voices of children, adult females, and adult males.
Voices may also differ in tone, making it impossible to create a blanket EQ for all voices. Instead, you may create an EQ that targets the average range of each voice:
|
✅Pro Tip: If you want a deeper presence, you can boost it to 2000-4000 Hz or higher. |
The car audio system includes an EQ that you can adjust to optimize your music listening while driving. Typically, the best equalizer setting for car audio is a balance of adequate bass and adequate highs.
However, this can still depend on personal preference and the sound of particular speakers in the car's audio system. The frequencies that control the bass will range from 32 Hz to 250 Hz on the equalizer settings.
While frequencies as low as 4 kHz can control the midrange, frequencies as high as 16-18, kHz can control the treble (or music sizzle).
|
✅Pro tip: Know the music before adjusting EQ settings. Different types of music require different EQ settings. Also, do not go overboard with your bass; it can interfere with your hearing because your car is so close. |
Audio affects the gaming community, as many shooter games rely heavily on audio cues like enemy footsteps. You can get an edge by making your gaming sound clearer to hear your opponents better.
Increasing the higher mid-range from 2000 Hz to 4000 Hz for FPS games can be helpful. For story-based games, the lower frequencies will need a boost to help the players feel their environment.
If you love listening to audiobooks and podcasts, optimizing your EQ for human vocals is the best equalizer setting for a clear voice.
Every person has a slight deviation in their tone, making finding the perfect equalizer settings for podcasts challenging.
You can consider the following equalizer settings:
If your TV comes with a graphic equalizer, you can tweak every sound according to your liking.
You can boost the equalizer at midrange frequencies for a more precise dialogue, like between 2000 Hz and 6 Hz. This can help amplify the dialogue and make it cut through better.
Another option is to cut it around the 300-800 Hz range. This area can make a voice sound warmer, but it can also make things muddy.
By cutting in this area, you may be able to make voices clearer and fix a muffled sound.
Apple Music is a good streaming app that you can tap to listen to your favorite songs and albums in high quality. Despite the platform's high sound quality, you can adjust your equalizer.
There is a built-in equalizer in Apple Music, and it has custom presets that let you change how the music sounds at different frequencies.
Feel free to play around with the other presets or make your custom settings to find the right balance of sounds for you.
Here's what some settings do:
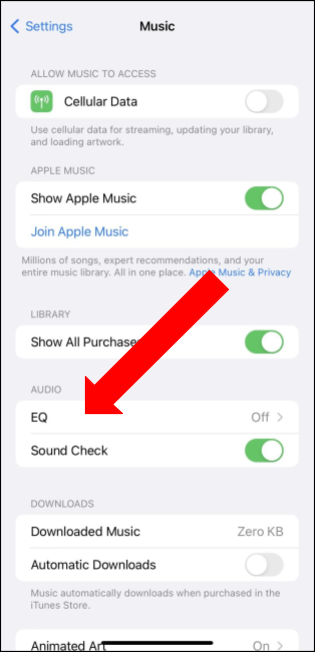
To find Apple Music EQ on your iPhone, follow these steps:

You can also set the Apple Music equalizer on your Mac. You can choose from 20 presets of the most commonly used frequency settings.
Adjust the settings manually, then save your customized settings as a preset you can use again.
To do this, follow the steps below:
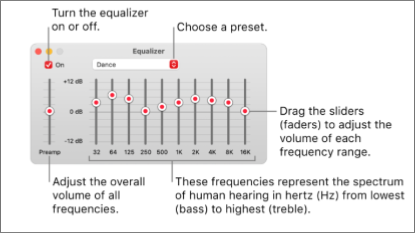 Image source: Apple
Image source: Apple
You may consider using Apple Music equalizer apps like Boom: Music Player and Equalizer. If you are looking for a finer equalizer with a better bass booster for music, the Boom Music app is worth a try.
Its immersive 3D surround sound, punchy equalizer presets, multiple library accesses, audio intensity control, and more make it great with or without headphones.
Spotify has a built-in equalizer that lets you choose from preset settings or manually change the frequency. The Spotify Equalizer has six bands you can move up and down, boost, or lower to a specific frequency.
Defining Spotify's best equalizer settings is difficult because they depend on your headphones, music genres, and personal tastes.
You can test each setting to find the ones that fit your tastes. Listen to your music and tailor the equalizer to your liking in real-time. Here are some of the best settings for Spotify:
|
📝Note: To learn more about Spotify, Techjury has several articles about it. Read our article on How Much is Spotify? [Spotify Pricing Explained in Detail] and How To Unblock Spotify - 3 Easy Methods Explained |
The genre influences what you can comfortably tweak regarding the best equalizer settings for music. Presets can help you figure out where to begin in most genres.
Below are some genre-specific equalizer setting ideas:
If you love pop music, you should keep the vocals and mid-ranger as clear as possible. Concentrate on boosting the mid-range frequencies and a little of the low-mid and high-mid frequencies, as shown below:
 Image source: Descriptive Audio
Image source: Descriptive Audio
Rap music is a genre known for its rhythmic storytelling and expressive lyrics. To achieve the best, boost the low-end to emphasize powerful basslines and enhance the vocals for clarity and impact.
Rap music relies heavily on a powerful and tight bass foundation. The best equalizer settings for rap music include a boost in the 64 Hz region, especially if the kick stands out.
Rap lyrics are important, so mid-range frequencies from 2000 to 6000 Hz highlight vocals.
Making the best EQ settings for hip-hop is an art that involves capturing the unique energy and spirit of the genre.
Emphasize frequencies around 80 to 120 Hz to keep the kick drum prominent. Avoid muddiness by lowering low-midrange frequencies between 150 and 350 Hz.
You can focus on as many electric guitars and bass drums as possible for rock music. Boost the low and high-frequency ranges while keeping the midrange adjustments as low as possible.
Here’s an example of an equalizer setting for rock music.
 Image source: Descriptive Audio
Image source: Descriptive Audio
Setting frequencies with an equalizer for acoustic music enhances each instrument's natural qualities and ensures a balanced and refined listening experience.
The goal is to get a balanced sound that keeps the natural qualities of acoustic instruments while reducing harshness. Increase the bass, mid-ranges, and highs slightly to clarify instruments and vocals without sounding unnatural.
 Image source: Audio Solace
Image source: Audio Solace
In the next section, you will find some helpful tips for configuring equalizers.
Fine-tuning frequency bands lets you fix audio imbalances, emphasize certain elements, and customize the sound. However, if you approach EQ too aggressively, things can go wrong.
Extreme or incorrect frequency adjustments can cause distorted audio, overpowering elements, and unnatural sound representation.
Here are some tips to help you achieve the sound you want:
You can improve your audio customization abilities by incorporating these EQ tips into your arsenal. It could produce a refined and captivating sound that enhances the listening experience.
Patience, experimentation, and a willingness to refine your techniques are keys to mastering the art of EQ.
A good equalizer setting can genuinely change the way you hear sound. EQ allows you to craft the best EQ settings for various devices and genres to achieve a balanced and impactful mix.
While there are some guidelines for achieving a balanced sound, the best settings are subjective and often based on personal references.
The ideal frequency settings largely depend on individual preferences and the specific characteristics of the audio equipment used. Play around and try different settings to see what works best for you; that is the perfect setup for you!
The range of frequencies that are considered safe for humans falls between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. This range is referred to as the audible frequency range.
In general, adding EQ before other effects like compression or reverb is recommended. EQ shapes the tone and frequency balance of the sound, and other effects are often applied to modify the processed audio.
Yes, EQ can help improve the sound of your headphones with minimal effort. You can make the sound clearer on the spot, and you can always alter the setting to fit your liking best.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 08, 2024
Updated · Feb 05, 2024