
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Sep 06, 2023
Aditya is an Azure DevOps and Infrastructure Virtualization Architect with experience in automation,... | See full bio
Terry spends her time researching all things digital — from marketing through online business crea... | See full bio
External storage is non-volatile data storage outside a computer's internal components, often called an external drive. These drives are frequently connected to computers through USB, eSATA, or FireWire. It can be removed and accessed elsewhere.
Examples of external storage are floppy disks and optical discs, compact flash drives (USB flash drives and memory cards), portable storage devices (external solid-state drives and enclosure hard disk drives), and network-attached storage.
In this article, you will learn more about the basics of external drives, their types, pros and cons, and their significance in the digital world.
|
Key Takeaways 🔑 A compact disc, or CD, is a flat, round optical storage medium invented by James Russell. 🔑 If you use DVD, no unwanted data alteration can occur during the transfer because it is not permitted to re-write data to disc. 🔑 External drives are available in various sizes and interfaces, including USB, e-SATA, and Firewire. 🔑 An HDD resembles an airtight case containing one or more platters and an arm with several heads. 🔑 Currently, three storage systems are available: external, internal, and cloud. |
All data storage not housed in a computer's primary storage or memory is stored on an external storage device. Its equipment might be temporary or permanent, detachable or non-removable, and wired or wireless in how it connects to a network.
External storage allows users to segregate data from a computer's primary storage and memory at a reasonable cost. It expands storage capacity without requiring the system to be opened.
In 1953, IBM recognized the immediate application for a "Random Access File" with a high degree of rapid random access at a low cost. The engineers at IBM's San Jose, California, laboratory invented the hard disk drive after considering technologies such as:
The minicomputer age ended when PCs were released in the 1980s. As a result, the industry sought more capacity manufacturers such as IBM, DEC, and Hewlett-Packard to continue to produce external hard drives.
Apart from their history, external storage devices have evolved. Find out the different types of external drives, their pros and cons, and how to find the proper external storage.
As technology progresses, various kinds of external storage emerge. This ranges from CDs, DVDs, external hard drives, flash drives, and memory cards.
You can delve more into each external drive. Continue reading!
A compact disc, abbreviated as CD, is a flat, round optical storage medium invented by James Russell. On August 17, 1982, the first CD was manufactured at a Philips factory in Germany. The image depicts the bottom of a standard compact disc, the side the disc player reads. A label on the opposite side of the disc indicates what is on it.
Compact discs, although an old technology, still have advantages. Here they are:
Along with their advantages, CDs also have disadvantages because they have remained obsolete due to emerging technologies in data storage. Some of its cons are:
A digital versatile disc, or digital video disc, is a disc that can contain far more data than a typical compact disc. DVDs are commonly used to store and view movies and other data.
The first DVD-ROM drives that used these discs were sold in 1997.

DVDs are still present in today’s technology because of some of their advantages in data storage. Here are some of its pros.
DVDs also have disadvantages, mainly when data requires high storage capacity. Some of its cons are.
The simplest and most affordable way to add more storage, whether for media storage or to back up your computer, is with external hard drives.
This external storage device requires only a USB cable attached to your computer, making it convenient to use and carry with a laptop in multiple locations.
Desktop external drives are available in various sizes and interfaces, including USB, e-SATA, and Firewire.
Most external hard drives are typically SATA-based, but you can pay more for an SSD (Solid State Drive) model for increased speed.

External hard drives make storing data more convenient and easily accessible. Here are some of the pros of external hard drives.
As with any other data storage device, external hard drives could be better but have their share of cons. Here are some of them.
|
👍Helpful Article: If you want to find out what SSD you have, this article will give you easy techniques. |
For external drives, there are two types. One is the Hard Disk Drive (HDD), and the other is the Solid-State Drive (SSD).
Learn more about HDDs and SSDs. Continue reading!
|
HDD |
SSD |
|
It uses mechanical spinning disks and a moving read/write head to access data. |
Uses memory chips. |
|
Slow |
Fast |
|
More storage capacity. |
Less storage capacity. |
|
Cheaper |
More expensive. |
|
Best for storing large amounts of data like documents, movies, and photos. |
Best for storing apps and operating systems. |
A hard disk drive (HDD) resembles an airtight case containing one or more platters and an arm with several heads (transducers). Data is stored on a platter covered with a magnetic substance and is written and read using heads that move over the platter as it spins.
An HDD is a low-cost solution for storing large amounts of data you will not need daily.
SSDs, or Solid-State Drives, have no moving parts. They store data on flash memory chips, similar to USB thumb drives. An SSD and a memory chip have a controller chip that locates the requested data.
An SSD is better if you intend to use an external data storage device for photo or video editing and require quick file access.
Unlike an optical or standard hard disk, a flash drive is a compact, ultra-portable storage device with no moving parts. This type of external drive is sometimes called a pen, thumb drive, or jump drive.
Flash drives connect to computers and other devices through a built-in USB Type-A or USB-C socket, resulting in a USB device and cable hybrid.

Flash drive portability is one of their advantages, but it doesn’t stop there. Other advantages of flash drives include the following:
Flash drives also have their fair share of limitations and disadvantages. Here are some of its cons.
A memory card is a storage device used to save media and data files. It is a persistent and non-volatile storage medium for data and files from the associated device. Memory cards are widely used in portable devices like cameras and phones.
It is primarily used in mobile phones, cameras, and other portable and handheld devices as primary and portable flash memory. PC Cards (PCMCIA) were the forerunners of current memory cards when they were commercially introduced.
Besides offering non-volatile media storage, a memory card employs solid-state media technology, which reduces the likelihood of mechanical difficulties such as those seen in traditional hard drives.
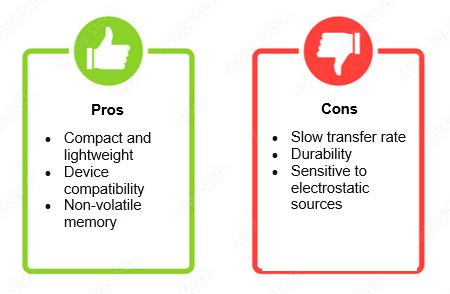
Memory cards are one of the smallest data storage devices there are. It may be small, but it has several pros for data storage. Here are some of them.
Although memory cards are the most recent development in data storage, they also have cons that will make you think twice about buying them. Here are a few of them.
|
🎉Fun Fact: TransFlash, or TF, is essentially the old moniker for what is now known as a microSD card. It was created by Motorola and SanDisk and released in 2005. |
Now that you have learned about the various types of external drives, it is also essential for you to know the differences between external storage, internal storage, and cloud storage.
There are three storage systems: external, internal, and cloud. You must choose these three options when you want to store, secure, and protect your data.
Before you decide what data storage system to use for your data, find the similarities and differences below.
|
External Drive |
Internal Drive |
Cloud Storage |
|
|
Security |
Data security is quite strong. Hackers can only access your hard drive if it is connected to your computer. |
Encryption is available but might slow the computer process. |
To protect your data before it leaves your devices, secure cloud solutions now have unbreakable encryptions so that even if a hacker had your data, they would be unable to access it. |
|
Cost |
You can get terabytes of storage for at least $100. |
More expensive than an external drive. |
You need to pay for a monthly subscription. |
|
Sync Technology |
Automatic backup software can be used. However, your external drive must be permanently attached for this to work. |
No sync technology is needed unless manually backed up or used with backup software. |
It has sync technology that automatically uploads new or modified files to your storage space. There is no need to worry if your files have been backed up. |
|
Universal Access |
Many wires are involved when transferring files from one device to another. It’s not a backup you can easily set up on the go. |
You need an external storage device to transfer files. |
You only need an internet connection to transfer files to and from the cloud. |
Now that you have learned the differences between the three storage devices, you must also know how to choose the right external drive.
Storage space is arguably the most essential factor when purchasing an external drive. Acquiring a high-speed gadget with encryption and remote access is only worthwhile if it can hold some of your data.
Transfer speed is also highly significant. If you frequently transfer data to a large drive, you don't want to wait forever for the transfer to complete.
Mobility is vital to keeping your drive with you when out and about. It should be lightweight and compact enough to fit in a pocket or backpack and be easily accessible. You also want one that does not require an extra power cable.
Current external drives frequently feature rigid enclosures to protect them from damage. But it is wise to choose an SSD because it has moving parts. An SSD is more resistant to drop harm than a standard hard drive and, thus, far more durable.
External hard disk drives are slightly more expensive than internal hard disk drives, and your budget will help you decide whether to go with a desktop-bound solution or a more portable one.
Suppose you have already chosen the best external drive for you. In that case, it is also essential that you know how to take care of and maintain your external drive to preserve your data.
Taking care of your external drive is important because it stores your data. To make sure this data is secured and preserved. You must observe proper methods to maintain your external drive.
Here are some tips for maintaining your external drive.
External storage offers more space, portability, and the ability to share data between devices. It is available in various formats, including CDs, DVDs, external hard drives, flash drives, and memory cards, each with advantages and disadvantages.
External drives are also very different from internal drives and cloud storage, each with perks and cons.
After learning all these facts, you should know how to care for your external drive to protect and secure your data.
Yes, you can use an SD card as external storage by using a memory card adapter and connecting it to your PC.
It is usually safe to leave a portable external hard disk plugged in and active 24/7 but ensure proper ventilation to avoid overheating.
Data can be stored on an external drive for about 3 to 5 years or until your external drive stops working.
Solid-state drives also have a longer lifespan—up to ten years. Hard disk drives survive between 3-5 years.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 08, 2024
Updated · Feb 05, 2024



