
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Aug 17, 2023
Muninder Adavelli is a core team member and Digital Growth Strategist at Techjury. With a strong bac... | See full bio
Lorie is an English Language and Literature graduate passionate about writing, research, and learnin... | See full bio
VRAM, short for Video Random Access Memory, is a special memory in your computer's graphics card that helps display images. Having more VRAM improves performance.
Similar to your computer's central brain (CPU), which uses regular memory (RAM) for programs, the graphics brain (GPU) uses VRAM for images and actions sent to the screen via HDMI.
Think of your computer as having two memory types: one for long-term storage (storage drives) and one for immediate tasks (RAM and VRAM). In essence, VRAM serves as active memory for graphics, enhancing game visuals and task speed.
Discover everything about your computer's graphics card, including what a VRAM is, its functions, and optimization, in this helpful guide.
|
🔑Key Takeaways:
|
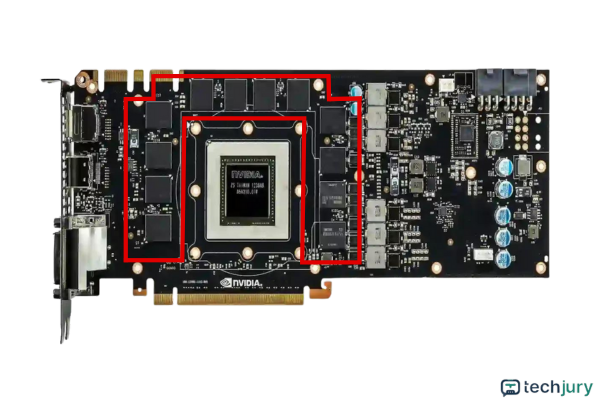
VRAM stores high-speed image data for screen display. It's crucial for graphics-intensive tasks like gaming and creative work.
The amount of VRAM directly influences your PC's capability to handle complex images; more VRAM means better rendering.
VRAM is often called GPU memory and affects your graphics card's performance. Modern GPUs use GDDR6, GDDR5, or GDDR4 VRAM standards.
Let's delve into the types of VRAM, their impact on gaming and creativity, and how to choose the right amount for your needs.
In gaming, VRAM is vital since games demand varying VRAM amounts due to different resolutions. Extra graphics card memory is necessary to render high-quality images. Without it, textures overflow VRAM, leading to GPU spillover into RAM and poor and slow performance.
There is no best type of RAM, as different types have varying applications. Get to know about them below.
Samsung Electronics developed a fast type of RAM called WRAM, which is short for Windows RAM and supports two ports.
With this capability, a video adapter can access memory for display while new data is written, leading to quicker display than single-port RAM.
WRAM is akin to VRAM but offers even better performance at a lower cost. It’s due to the support for addressing large blocks (windows) of video mem
|
Purpose: WRAM is excellent for super sharp pictures such as 1,600 x 1,200 pixels using true colors. However, it's not connected to Microsoft Windows, though. It is used in the Matrox MGA Millennium video display card and can also be used elsewhere. |
Imagine a budget-friendly video memory that works well with the computer's clock. It's like having two pages open at once in a book.
This memory has 144 pins and connects to your computer at different speeds — 83 MHz, 100 MHz, 125 MHz, and 142 MHz — making it work quickly.
|
Purpose: SGRAMs are explicitly designed to handle tasks that need lots of graphics power, like smoothly making 3D pictures and playing videos. |
RDRAM emerged from Rambus in 1999, surpassing older memory types like Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM). While SDRAM handles data transfer at up to 133 MHz, RDRAM achieves up to 800 MHz speeds.
It goes by names like Direct RDRAM or Rambus. It consists of a RAM, a RAM controller, and a bus path connecting it to microprocessors and other PC devices.
RDRAM serves as a high-speed memory subsystem, excelling at data transfer.
MDRAM is a high-performance memory technology featuring small DRAM banks (32 KB each). It is connected to a shared internal bus through individual I/O ports.
This unique design enables simultaneous read/write operations on multiple banks, resulting in significantly faster performance than regular DRAM.
MDRAMs suit graphic tasks, sync for better performance, and cost less than other VRAMs due to their tailored memory capacity.
Introduced in 2000, GDDR (or GDDR SDRAM) has become the dominant graphics RAM, surpassing VRAM and WRAM.
Newer GDDR generations are faster and improved, but their numbering doesn't match DDR versions. For instance, GDDR3 uses DDR2 chips, GDDR5 uses DDR3, and so on.
This advanced type of VRAM is meticulously designed for the demanding needs of graphics-intensive applications.
|
👍Helpful article: To learn more about RAM, check out Techjury’s guides: |
Having laid the groundwork for the various types, let's explore the comparison between VRAM and RAM.
Understanding VRAM and RAM is crucial to boost your computer's capabilities. While RAM handles general tasks, VRAM optimizes graphics card performance for stunning visuals.
This table explores their essentials, compares their roles, and unlocks tips for maximizing VRAM performance.
|
RAM vs. VRAM: Side-by-side Comparison |
||
|
RAM |
VRAM |
|
|
What Is It? |
Memory component for temporary system storage. |
Memory component specialized in image data storage. |
|
Origin |
1940s |
1980s |
|
Primary Use |
Storage of temporary system files |
Storage of image data |
|
Influential Developers |
Freddie Williams & Tom Kilburn |
IBM Research |
|
Impact (Speed & Frequency) |
RAM has influenced techs like DRAM, SRAM, RDRAM, and DDR SDRAM. |
VRAM's development led to advancements in GDDR5, GDDR5X, and HBM. |
|
Upgradability |
Replaceable/Upgradable |
Usually not replaceable, soldered on GPUs |
Now that the lowdown on what is VRAM vs. RAM has been covered, time to dig into the fun stuff – how to check, boost, and level up your VRAM for some epic gaming action!
 Image source: GamerBTW
Image source: GamerBTW
Knowing what virtual memory is and how much available space is the first step in improving its performance.
The next step is to outline different methods to optimize VRAM, ensuring smooth graphics processing. The following techniques will be discussed in detail:
Updates to the graphics driver are vital to using VRAM best. Ensuring your graphics drivers are current improves compatibility, fixes bugs, and boosts speed.
Optimizing the image settings in a game is a crucial part of using VRAM. You can fine-tune VRAM allocation for a more fluid gaming experience by adjusting texture quality, anti-aliasing, and shadow resolution options.
Limiting background tasks is a smart way to free up VRAM for graphics, improving overall performance. By dedicating more VRAM to graphics-intensive programs, you ensure better functionality.
Keeping an eye on VRAM usage is important for better optimization. Doing this lets you make smart decisions and improve how VRAM is used.
Removing temporary files is another way to free up VRAM. Temporary files can build up and take up space, affecting VRAM. Regularly cleaning them lets you free up VRAM and ensure it's used well for graphics tasks.
Determining how much is available in your computer’s system is necessary before optimizing your VRAM.
Knowing your system's VRAM capacity lays the groundwork for optimizing its usage effectively.
For those uncertain about their VRAM capacity, several methods can help check the amount available.
Here’s how to do it:
An Nvidia GTX 1070 with 8GB of Display Memory (VRAM) is used in this case.
|
📝 Note: There are other ways to check how much your VRAM is, such as:
|
Getting a new or better graphics card is the way to improve your video performance.
Switching to a dedicated graphics card will significantly enhance video quality if your computer uses integrated graphics and runs slowly.
if you can't upgrade the graphics card, you can increase the dedicated VRAM in two ways.
Access your computer's BIOS and find Advanced Features or Graphics Settings options. Look for an option to adjust GPU memory allocation, typically set at 128MB by default. If possible, increase it to 256MB or 512MB.
|
📝 Note: Not all CPUs or BIOS versions offer this option. If it's unavailable, consider the workaround below. |
For integrated graphics, the Dedicated Video Memory value doesn't matter; it's fictional. Modify Registry to change VRAM reported to games, though it won't increase VRAM.
|
👍Helpful Article: If you can’t locate your Windows, this article might help you: Windows Button Not Working — 10+ Ways to Fix It |
Steps for Faking VRAM Increase in Windows:
These methods might not always work, but it's worth trying. Add more RAM or free up RAM for integrated graphics issues with limited RAM.
|
👍Helpful article: Upgrading RAM or video cards is easier on desktops. If you want to know more about this, read more here: How to Check RAM Speed and How To Boost It |
VRAM, short for Video RAM, is a special memory in computers that stores image data for smooth graphics display, especially in 3D programs and games.
Now that you know what VRAM is, its importance, and its usage, remember that it's just one aspect of your computer's performance — a weak GPU won't benefit from more VRAM.
For better gaming performance, consider having more VRAM. If an upgrade isn't possible, follow the steps above to trick your device into thinking it has more VRAM than it does.
8GB VRAM GPUs handle basic tasks but lack longevity. As games advance, more VRAM is needed for better performance.
You can't physically change VRAM, but optimizing its usage can help. It may not guarantee better performance, but it can be beneficial.
Warzone 2 system requirements vary. Competitive specs need 16GB RAM and 8GB VRAM, while ultra 4K specs demand 16GB RAM and 10GB VRAM.
A functioning graphics card lowers the frame rate. The app glitches and crashes if it mistakenly believes it has extra VRAM.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 08, 2024
Updated · Feb 05, 2024





