
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Jan 02, 2024
With a master's degree in telecommunications and over 15 years of working experience in telecommunic... | See full bio
After getting a master's degree in Literature, Publishing, and Mass Media, Teodora spent most of her... | See full bio
Cybersecurity has become a major concern for big and small businesses worldwide. People have grown more anxious about hackers releasing data due to several movies about it.
However, many seem to forget the potential threat that lurks inside the companies themselves, inside your home base–– yes, your own employees and business partners.
Insider threats are often overlooked. But they’re real-world cybersecurity incidents with more frightening consequences than the ones depicted in movies.
Insider threat statistics reveal that these dangers can come from employees, firm contractors, and other trusted associates.
Find out the latest insider threat statistics, its types, and the most notable encounters in history.
|
Editor’s Choice
|
Every 197 days, a data breach happens somewhere in the world, and some of them are caused by members of the company themselves.
Insider Threats are unarguably one of the most underestimated cyberattacks. Looking at the overwhelming 2023 cybersecurity data, recent developments and insider threat reports have indicated a rapid increase in insider attacks.
These have forced cybersecurity experts to pay closer attention to insider threats' damaging nature and reveal the business' need to invest heavily in cybersecurity.
Below are some mind-boggling statistics on insider threats.
(Soft Activity)
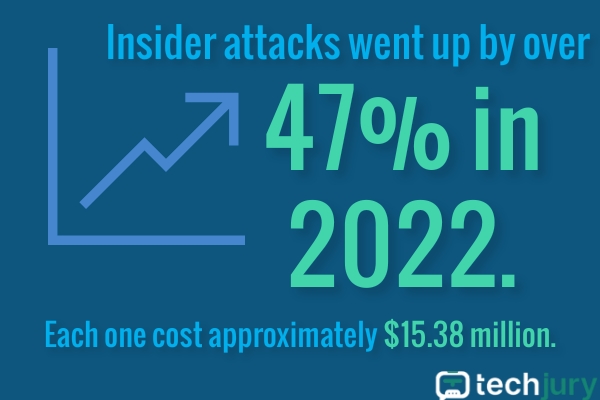
Insider incidents have risen 47%, costing about $15.38 million per single one. Credential theft took center stage from $2.79 million in 2020 to $4.6 million in 2022– an increase of 65%.
Reports found that 3/4 of respondents felt highly vulnerable to insider threats. 74% of organizations report that attacks increased by 6% compared to last year.
Identity security is crucial, not just for private citizens but for companies and organizations as well. As more entities become digitally aligned, they are more susceptible to insider threats.
(Soft Activity)
Although insider threats can come from malicious employees and contractors, the statistics reveal that most originate from plain carelessness.
People would send links from their Google Docs or Dropbox accounts without realizing they need to be secured. These documents get indexed on search engines and can easily be found by cybercriminals.
Employees should learn to encrypt any links they send with a username and password to prevent this.
|
🎉 Fun Fact: In 2016, a Snapchat employee got tricked into releasing payroll data from the company’s database. The employee got negligent and didn’t verify an email, falling for a phishing attack. The cybercriminal pretended to be Snapchat’s CEO, Evan Spiegel, requesting that the data be sent to him. |
(Soft Activity)
Users often reveal administrative data by mistake. A simple briefing on practicing security measures should suffice. However, threats from external attackers are rampant. Companies must invest in other cybersecurity solutions like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Endpoint Detection and Response tools (EDR).
(Cybersecurity Insiders)
Insider threats have reportedly increased in the last two years. Most businesses are now starting to keep an even closer eye on them.
Even if insider attacks frequently resemble external data breaches, cybersecurity, and IT experts have developed a deeper understanding of their differences. EDR security suits, for instance, give businesses a more accurate filter for identifying which attacks are internally caused.
(Ekran System)

Global cyberattacks increased by 38% from 2021 to 2022, making organizations feel unsafe. In fact, only 1 in 10 believe that their cybersecurity meets the needs of their business.
This reiterates the need for organizations to increase their budget allocations toward their cybersecurity needs. They also need to increase cybersecurity awareness among their employees through training, drills, and standard operating procedures (SOP).
(Ekran System, CISA)
Insider attacks are devastating. Not only are sensitive data criminally disclosed, but dangerous behaviors can also sprout from them.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has identified that insider attacks can manifest as damage through these behaviors:
(Soft Activity)
According to insider threat statistics, many businesses are affected by these attacks each year.
Internal threats target more and more businesses because of their employees’ expertise in the organization's system and exclusive access to sensitive information. This opens the doors for data thieves to carry out the exfiltration of critical information. For example, 30% of bankruptcies are due to employee theft.
To minimize this, companies need to raise security standards in their systems and among their workforce.
(Haystax, IBM)
Even though negligent employees cause more insider threats, business owners are more concerned about cybersecurity factors beyond their control.
In 2022, the global average cost for a data breach went up to $4.35 million. According to an IBM study, this attack has affected 17 countries and regions across 17 industries.
Sadly, there is no end in sight, as cybercriminals keep discovering new skills and techniques for their nefarious deeds.
|
✅ Pro Tip: Securing the network is the first step to fighting against a data breach. Explore the following solutions for your business. Mix and match those that fit your cybersecurity needs: |
(Trip Wire)
A Fortinet survey revealed that the three main insider risks are fraud (55%), financial gain (49%), and IP theft (44%).
Additionally, the finance department (41%), the customer access department (35%), and the research and development department (33%) are the most vulnerable to these attacks.
Hackers, especially black hats, mainly attack these departments for monetary gain, corporate sabotage, espionage, and trade secrets.
(Soft Activity)
Most insider attacks have occurred in industries like finance and insurance (38%) due to contractor crimes or errors. External contractors are given the same top-level network access privileges as corporate workers, which they have been known to abuse.

Internal attacks perpetrated by trusted business partners cause more financial havoc as they know the organization's inner workings and trade secrets. The level of betrayal involved in this attack also creates emotional and mental stress.
A 2023 global security trend aims to fix this by encouraging companies to request more accountability from third-party vendors.
(Zippia)
Businesses are paying for cybersecurity solutions. However, identifying a cyberattack or a breach usually takes 212 days, while containing it takes roughly 75 days.
Pinpointing a breach can also take months before the organization notices it. By then, the damage level has already grown.
Additionally, recovering from an insider attack can span approximately 6 months or even more, depending on how much damage was inflicted.
(Checkpoint)
Cybercrime has risen by 38% in 2022. It has become so prevalent that every 39 seconds, a hacking incident is happening somewhere in the world.
The top 5 cybercrimes are extortion, identity theft, personal data breaches, non-payment, and phishing attacks. Such attacks take 1% of the Global GDP and will cost $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
Data loss and privacy were the top worries for over 60% of cloud security experts polled for the 2022 Cloud Security Report.
This unsettling trend highlights the ever-evolving tactics of cyber criminals and their exploitation of vulnerabilities across sectors.
(Soft Activity)
When discussing insider threats, people mostly think of a vengeful employee on a malicious rampage. Still, some negligent or credentialed insiders knowingly or unknowingly share their login details– leading to many data breaches.
According to insider threat statistics, 67% of data breaches result from stolen credentials. Plus, credential leaks increase by a massive 129% year-over-year, further pushing the need for extensive cybersecurity training for any workforce.
|
“Reacting to data breaches requires more than just technical expertise. It requires legal and communication support. An organization must have a communication plan when a data breach or cyber-attack happens.” ― Magda Chelly, Cybersecurity expert, to Medium |
With the recent surge in insider data breach cases, more businesses are now experiencing attacks inside their cyber walls.
Below are the relevant insider data breach statistics for 2023.
(Get Astra)
Only 1 in 5 IT professionals believe insider attacks are a security concern. In addition, only 39% of businesses have a group of cybersecurity specialists that understand information security well enough to assess risks and properly implement preventative measures.
This is why internal security breaches are a constant problem for US companies. Employers, IT staff, and employees can disregard security protocols.
|
🎉 Fun Fact: eBay, one of the largest e-commerce companies in the US, experienced one of the biggest data breaches in history in 2014. Hackers got hold of employee login credentials and stole information and encrypted passwords from 145 million eBay customers. |
(Business DIT)

91.5% of data breaches are directly attributable to human mistakes. Whether it’s stolen credentials, phishing, misuse, or simple errors, people have always played a significant role in these occurrences.
End users, system administrators, and developers must be more security conscious while using their organizations’ security information.
Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly expensive as cybercrimes are upgrading, turning into more complex schemes. In 2023, the global cost of cybercrime is set to pass $8 trillion in just one year. Clearly, if a company isn’t willing to invest money in this problem, they’ll put themselves in a vulnerable position.
Here’s the money trail on cybersecurity and insider threats:
(ARN)
In 2022, the risk management and cybersecurity expenditure was $17 billion higher than the previous year. That’s because 69% of firms have now decided to allocate more funds. Additionally, 26% plan to increase their budgets by at least 10%.
A lot of businesses are stepping up their cyber security efforts. 9 of 10 organizations have at least one cybersecurity team and have delivered training sessions for staff and volunteers indirectly involved in cybersecurity.
They’re doing it for various reasons, though. About 49% invested more in cybersecurity just for compliance. 35% did it due to security incidents, while 38% because of digital transformation risks.
(2022 Cost of Insider Threat Global Report)
It took up to 85 days to stop an insider threat from causing more damage in 2022. Moreover, the average cost of each data breach or insider threat was $184,548. The ex-post analysis is the least expensive at $26,563.
Monitoring and surveillance cost $35,000, the lowest of the expenditures. However, it still has one of the highest net increases.
All figures shot up to 114% from 2016, showing how severe and cost-intensive this threat is.
|
✅ Pro Tip: Regular cybersecurity training on your team is the most cost-effective and budget-friendly solution to fighting insider threats. Do this at least once every quarter. |
(Observe IT)
Over half of organizations experienced at least one internal attack in 2022, spurring them to spend nearly 60% more than they did three years ago to recover.
Increased cybersecurity measures against insider threats are mainly driven by investigation and detection. Organizations have dedicated a specific budget for these primary drivers, as insider threats pose as much threat as external bodies.
(Proofpoint)
On average, financial institutions have spent around $21.25 million on insider risks–– a 47% increase from the previous year. Meanwhile, retail enterprises' costs have skyrocketed by 62%, reaching around $16.56 million.
Hackers mainly target financial institutions like banks, credit agencies, retail outlets, and e-commerce stores. They usually go after people's card and payment information on websites. For instance, 4,800 websites are hacked and infected by formjacking attacks each month, with perpetrators walking away with credit card numbers and login information.
(Observe IT)
Insider threat statistics reveal that larger organizations with a workforce of 75,000 and above have spent an average of $17.92 million on these cases.
On the other hand, smaller organizations with a workforce of 500 or fewer spent $7.68 million on the exact cause. Of course, a larger organization means more data losses, more damage, resources, and manpower to employ than smaller organizations and businesses.
|
Fun fact: In 2022, Microsoft, one of the largest companies in the world, got hit by an insider attack. Multiple employees had leaked login credentials to the company’s infrastructure on GitHub. The act would have endangered the entire company, allowing criminals access to Azure servers and other internal systems in Microsoft. |
As mentioned, insider threats can take many forms, including physical harm, espionage, sabotage, theft, and cybercrime. Hackers always develop new ways of carrying out operations, and keeping up with them can be challenging.
(Soft Activity)
In 2021, 323,972 phishing incidents were recorded. It remains one of the oldest and most effective ways for hackers to penetrate a network.
Phishing is a common social engineering technique and a prominent cause of insider threats. Emails of this nature are designed to trick users into clicking on a corrupt file or filling out survey forms containing confidential information, to be used for selfish gains.
Employees who fall for phishing unintentionally transfer essential business data to malicious individuals through fraudulent websites.
(Source: CSO Online)
One of the most effective types of cyberattacks is via malware, and it’s still primarily spread through emails.
Most spam emails contain different types of malware. They include intriguing subject lines and appealing headers that entice the recipient to open and click the email.
Insider threats and their propensity to commit millions of damages have made indelible marks in the cybersecurity industry. Here’s a list of the most prominent ones, forever remembered as some of the most impactful incidents in history.
1.) In 2013, Edward Snowden, a security operative and subcontractor for the CIA, used his CIA authorization to expose classified documents that shook the world.
This resulted in the implication of the National Security Agency (NSA) and the Five Eyes (FVEY), comprising the US, UK, Canada, New Zealand, and Australia.
His actions brought to light the mass surveillance of the US, UK citizens, and citizens of other nations being carried out by the NSA and FVEY.
The case of Edward Snowden is a typical example of how dangerous and effective an insider threat can be. But accordingly, he did it for the good of the people.
2.) With her former Amazon Web Service (AWS) employee skills, one lady hacked her employer, the Capital One Company, and numerous other companies.
According to several reports, this woman took the social security numbers of 140,000 people, 1 million Canadian Insurance Numbers, 100 million customer Personal Identifiable Information (PII), and 80,000 bank account numbers.
3.) A structural engineer named Greg D. Chung stole documents about the US government's military and aerospace programs from 1979 to 2006. He intended to deliver them to China. It was suspected that he was a spy sent to steal government secrets.
4.) The Punjab National Bank attack is one of the costliest insider attacks ever recorded.
Using the Swift interbank communications system, a worker authorized the transfer of £1.5 billion or $1.84 billion through letters of undertaking and international letters of credit.
|
⌛ In a Nutshell: Many companies and organizations have seen their fair share of internal attacks committed by once-trusted employees over the years. These employee-turned-attackers have leaked information to the public, stolen sensitive information, and cost billions of dollars in damages. |
There are several types of insider threats. The most common ones are outlined in more detail below.
These types of insider threats are employees who, despite receiving training and instructions, choose to ignore cybersecurity protocols. They do whatever they feel like on the server, placing the whole network at risk.
These employees have no intent to harm the organization. Still, their actions are capable of causing a lot of damage.
These are employees or close associates that intentionally cause harm to an organization by exposing sensitive business data to external threats or using it for personal gains.
These employees do their regular tasks without malice, loyally following organizational policies. However, unbeknownst to them, they might already be infected with several types of malware, placing the whole organization at risk.
These employees are the prime target for tailgating. It’s where people with malicious intent pretend to be legit employees and ask for credentials from unsuspecting insiders to enter a restricted space.
Inside agents are employees in partnership with hackers to gain access to workplace servers. They either steal from their employer's server or assist a third party in infecting the server with malware.
Insider attacks are harmful and challenging to identify because these people already have access to your network and the company files and folders.
These threats can either be deliberate or unintentional. Insiders with grudges, those seeking financial gain, or those merely intending to sabotage an organization can all make deliberate threats.
|
“Cybersecurity is a social responsibility. We all have a role to play.” ― Magda Chelly, Cybersecurity expert |
Although often overlooked, inside threats pose as much danger as external threats. If not, a bigger one.
The frequency of insider threats is ever-increasing. Thankfully, more businesses are now beginning to understand their nefarious nature. Many businesses are now conducting initial investigations on prospective employees to mitigate potential risks. This is a simple task with the help of various background check apps.
Cybersecurity Insiders is an online community of over 500,000 information security professionals across the globe. They aim to provide organizations with everything related to cybersecurity.
Insider threats make up 60% of cyber attacks in the world. They are sometimes overlooked or considered external threats because they can be challenging to detect.
Examples of insider risks include employees who improperly dispose of critical documents, sell confidential information to rivals, unintentionally click on a link, or open phishing emails that contain viruses.
Insider threats could harm your business if they aren't detected on time. Malicious insider threat statistics show that the longer an attack goes undetected, the more harm it does to a firm.
Your email address will not be published.
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 11, 2024
Updated · Feb 08, 2024
Updated · Feb 05, 2024



